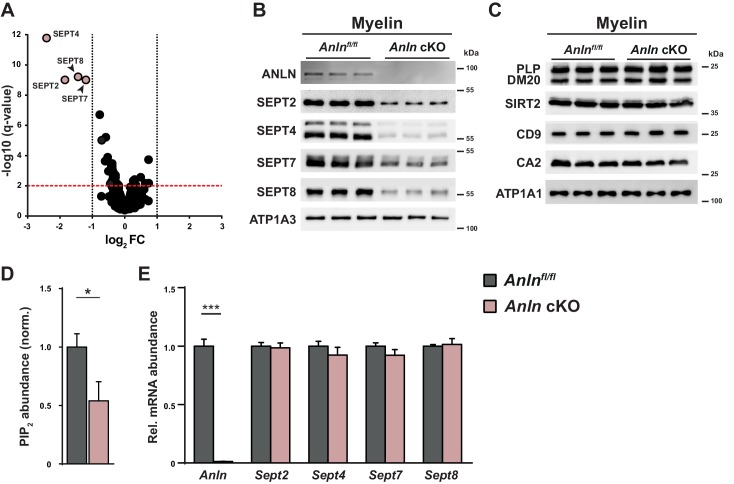
Figure 3. Myelin composition in mice lacking oligodendroglial expression of ANLN.
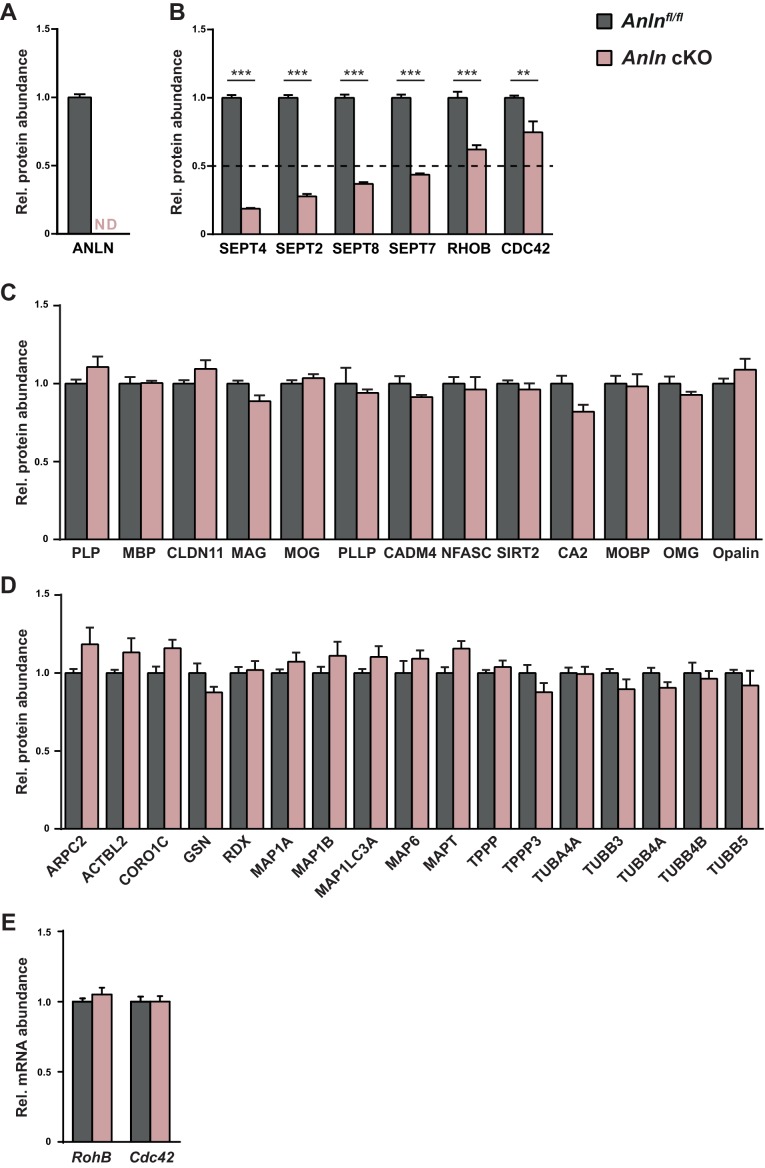
(A) Volcano plot summarizing genotype-dependent quantitative myelin proteome analysis. Data points represent quantified proteins in myelin purified at P75 from the brains of Anln cKO compared to Anlnfl/fl mice (n = 3 mice per genotype). Data points are plotted as log2-transformed fold-change (FC) on the x-axis against the −log10-transformed q-value on the y-axis. The horizontal red dashed line indicates a q-value of q = 0.01; the vertical black dashed lines mark the ±1 log2 fold-change threshold indicating a halved or doubled abundance of a protein in myelin, respectively. Data points representing myelin septin monomers (SEPT2, SEPT4, SEPT7, SEPT8) are highlighted in light red color with protein names given; note that their abundance is strongly reduced in Anln cKO compared to Anlnfl/fl myelin. Also note that ANLN is not represented because it was not detected in Anln cKO myelin. For bar graphs showing genotype-dependent comparison of the abundance of individual proteins in myelin see Figure 3—figure supplement 1A–D. For the original dataset and exact q-values see Figure 3—source data 1. (B) Immunoblotting validates the lack of anillin (ANLN) and the strong reduction of septins (SEPT2, SEPT4, SEPT7, SEPT8) in myelin purified from the brains of Anln cKO-mice. ATPase Na+/K + transporting subunit alpha 3 (ATP1A3) was detected as control. Blot shows n = 3 mice per genotype. (C) Immunoblotting indicates that the abundance of classical myelin proteins (PLP/DM20, SIRT2, CD9, CA2) is unaltered in myelin purified from the brains of Anln cKO-mice. ATP1A1 served as control. Blot shows n = 3 mice per genotype. (D) Genotype-dependent quantitative assessment of PtdIns(4,5)P2 (PIP2)–levels in myelin purified from the brains of Anln cKO-mice compared to controls (Anlnfl/fl) at P75. Mean +/SEM. n = 6 mice per genotype; two-tailed unpaired t-test; PtdIns(4,5)P2p=0.0435. (E) qRT-PCR to determine the abundance of mRNAs encoding anillin and myelin septins in the white matter (corpus callosum) of control (Anlnfl/fl) versus Anln cKO-mice. Note that Anln mRNA was virtually undetectable in Anln cKO-mice while the abundances of Sept2, Sept4, Sept7 and Sept8 mRNAs were unaltered. Mean +/SEM. n = 6 mice per genotype; two-way ANOVA; Anln p<0.0001, Sept2 p>0.9999, Sept4 p>0.9999, Sept7 p>0.9999, Sept8 p>0.9999.