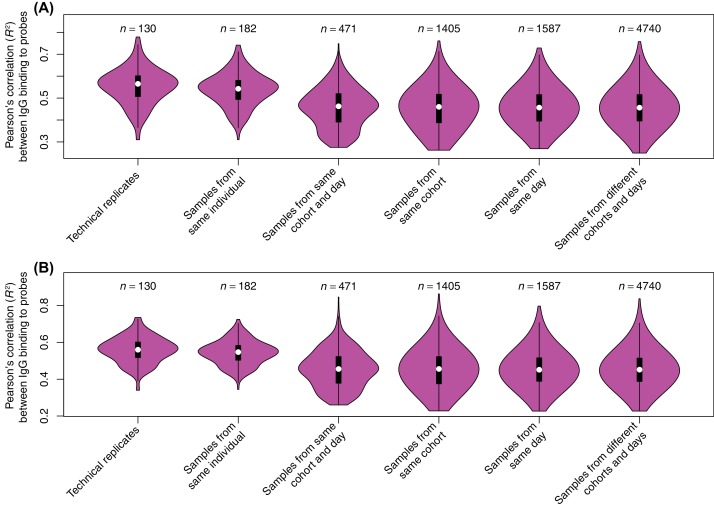
In a pilot experiment, the serum samples were applied to an array consisting of probes representing the proteome of
Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4. These were also present on the panproteome array, but they were not included in subsequent analyses. These two independent experiments provided an estimate of the variation between technical replicates, although the differences in the array designs means there is substantial systematic variation between them. The Pearson correlation (R
2) was calculated between all pairwise comparisons from the two sets of replicates, and the overall distribution for different types of comparison shown as violin plots for (
A) all probes and (
B) the 1165 immunoreactive probes (a maximum IgG binding of at least one across the
S. pneumoniae TIGR4 probes from the panproteome dataset). There was no significant difference between the correlations observed across all probes for technical replicates and other comparisons between samples from the same individual (Wilcoxon rank sum tests;
N = 312,
W = 13239, p = 0.073 for all probes). However, restricting the analysis to the immunoreactive probes found technical replicates to exhibit a significantly stronger correlation with one another, relative to samples from the same individual at other timepoints (
N = 312,
W = 13480, p = 0.036 for immunoreactive probes), consistent with the WCV-induced changes associated with antibody-binding target being reproducibly detectable. This high similarity between technical replicates and samples from the same individual is necessary for the persistence of an immune fingerprint in longitudinal samples (
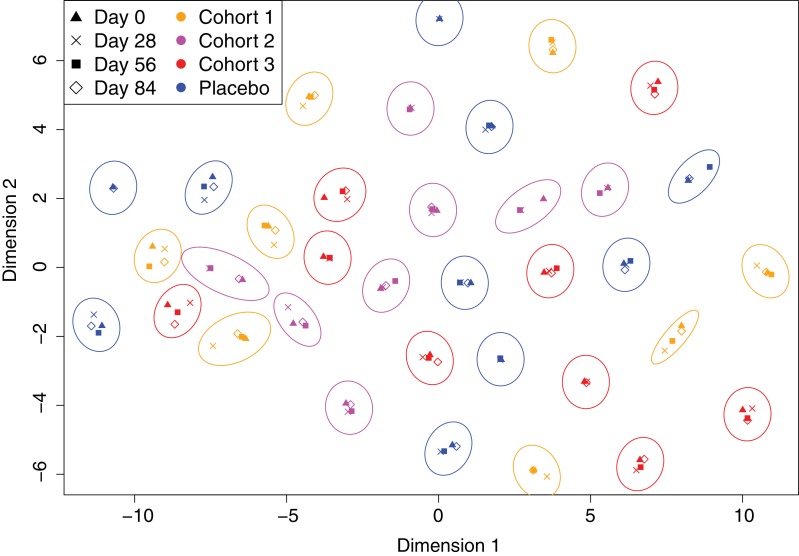
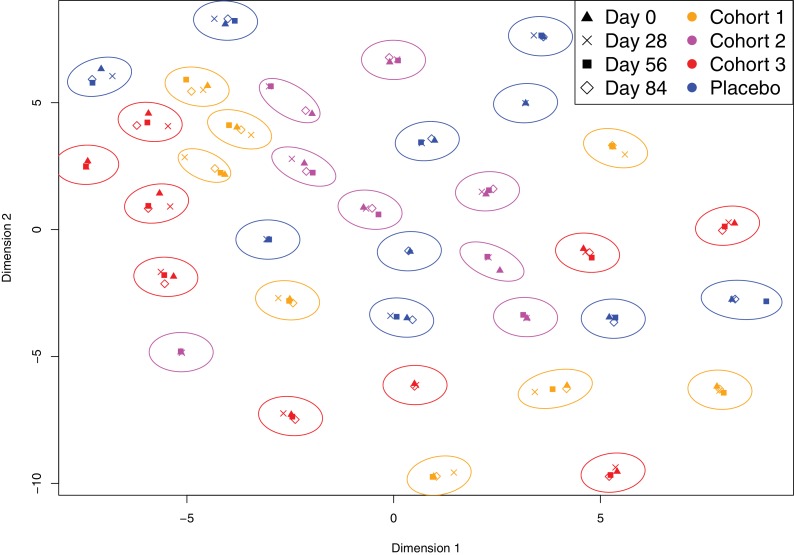
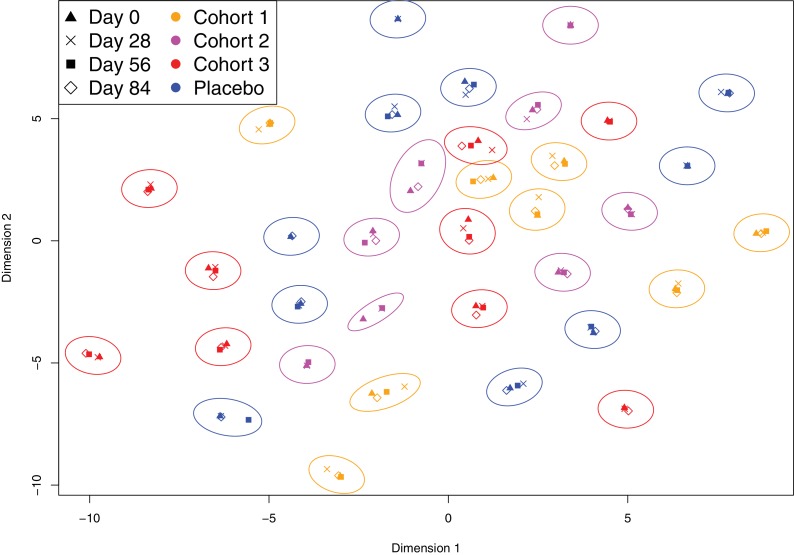
Figure 2). Comparisons between these two categories were significantly more correlated than comparisons with the next most similar category, different individuals in the same cohort at the same timepoint (Wilcoxon rank sum tests;
N = 601,
W = 48170, p < 10
−16 for all probes;
N = 601,
W = 48738, p < 10
−16 for immunoreactive probes). As there was relatively little variation between technical replicates, but reproducibly high variation between trial participants, biological replicates were prioritised over technical replicates in designing the study.