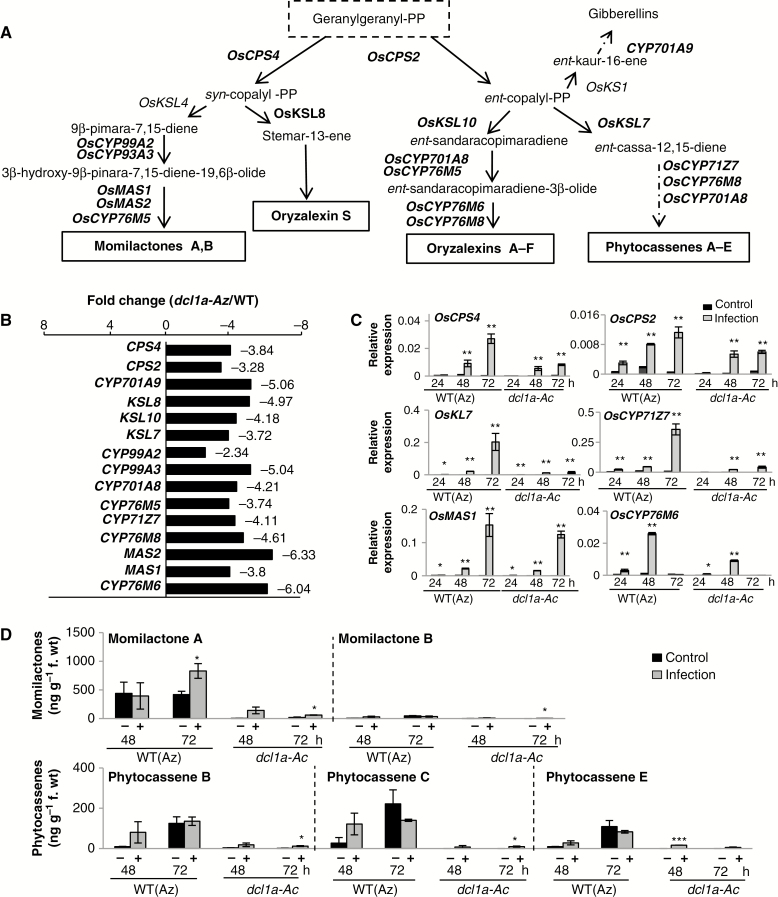
Fig. 4.
Expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of diterpenoid phytoalexins in dcl1a-Ac plants. (A) Biosynthetic routes of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. Genes with expression downregulated in dcl1a-Ac compared with wild-type plants are indicated in red. Diterpenoid phytoalexins are synthesized from geranylgeranyl diphosphate (geranylgeranyl-PP), which is sequentially cyclized by the diterpene synthases CPSs (copalyl diphosphate synthases) and KSLs (termed kaurene synthase-like because of their similarity to the corresponding enzyme in gibberellic acid biosynthesis), then converted to each phytoalexin by P450 monooxygenases (CYPs) and dehydrogenases. OsCPS4 (syn-copalyl-diphosphate synthase 4, Os04g09900); OsCPS2 (ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase 2, Os02g36210); OsCYP93A3 (9β-pimara-7,15-diene oxidase, Os04g09920); OsCYP99A2 (cytochrome P450, Os04g10160); OsCYP76M5 (cytochrome P450, Os02g36030); OsCYP701A8 (ent-sandaracopimaradiene 3-hydrolase, Os06g37300); OsCYP71Z7 (ent-cassadiene C2-hydroxylase, Os02g36190); OsCYP76M8 (oryzalexin D synthase, Os02g36070); OsCYP76M6 (oryzalexin E synthase, Os02g36280); OsCYP701A9 (ent-kaurene oxidase, Os06g37224); OsKSL7 (ent-cassa-12-15-diene synthase, Os02g36140); OsKSL10 (ent-sandaracopiramadiene synthase, Os12g30824); OsKSL8 (stemar-13-ene synthase, Os11g28530); OsMAS (monilactone A synthase, OsMAS1, Os04g10000; and OsMAS2, Os04g10010). (B) Fold repression of expression (dcl1a-Ac vs. wild-type azygous plants) of genes involved in diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis. (C) Expression of phytoalexin biosynthesis genes in wild-type (azygous) and dcl1a-Ac plants in response to M. oryzae infection (1 × 105 spores mL–1) or mock inoculation (red and black bars, respectively) (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01 comparing the indicated genotypes or condition by ANOVA). (D) Accumulation of diterpenoid phytoalexins is compromised in leaves of dcl1a-Ac plants. Three biological samples for each genotype and condition were examined (*P ≤ 0.05; ***P ≤ 0.001 by ANOVA).