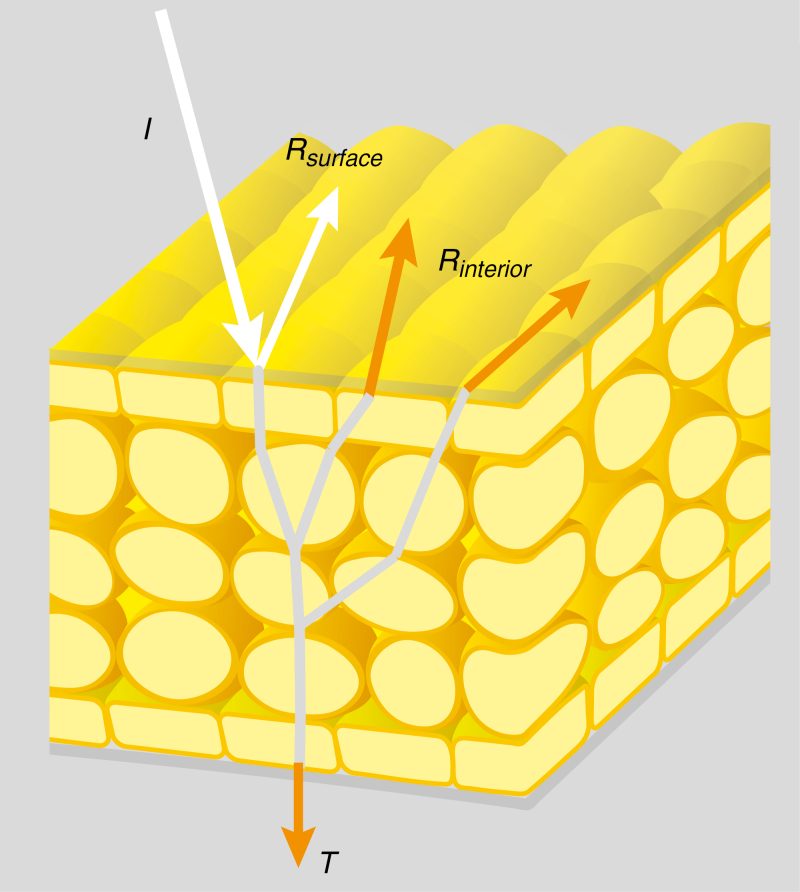
Fig. 1.
Diagram of light reflection in a flower. Part of the incident light (I) is reflected by the surface (Rsurface) or by the interior (Rinterior), part of the light is transmitted (T) through the flower, and light of a specific wavelength range is absorbed by pigments. The light that is reflected by the surface is largely unmodulated by pigments, whereas light that is reflected by the petal interior or transmitted through the flower will be modulated by pigments inside the flower (for visualization purposes the light rays inside the flower are shown in grey).