Figure 4. Specific excitation of dopaminergic neurons in the hypothalamic A11 attenuates trigeminal neuropathic pain via the activation of D2 receptor in the Sp5C.
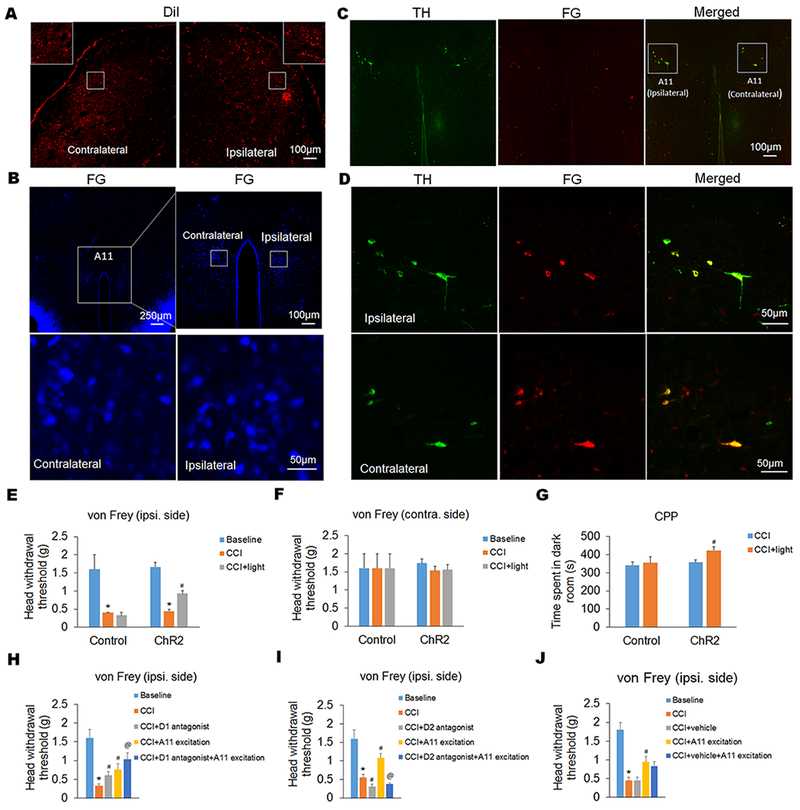
(A and B) By antegrade and retrograde tracing, we showed that descending projection from hypothalamic A11 to Sp5C was bilateral. Following unilateral injections of the antegrade tracer DiI into the A11 and the retrograde tracer FG into the Sp5C, DiI and FG were expressed in both sides of Sp5C (A) and A11 (B), respectively. The insets in (A) display higher magnification images of the respective boxed areas in the contralateral and ipsilateral Sp5C at low magnification. In the upper panel of (B), the right image represents the boxed A11 area in the left image at high magnification. And the lower panel of (B) displays the respective boxed areas in the contralateral and ipsilateral A11 of the upper right image at higher magnification. (C and D) By double staining, we showed that the descending projection from hypothalamic A11 to the Sp5C was dopaminergic (C). The retrograde tracer FG was co-expressed with TH, a specific marker for dopaminergic neurons, in both contralateral and ipsilateral sides of A11 nucleus (D). The expression of TH and/or FG in bilateral A11 was showed at low magnification in (C). And the expression of TH and/or FG in the ipsilateral and contralateral A11 within the respective boxed areas in (C) was showed at high magnification in (D). (E–G) By optogenetic stimulation of A11 dopaminergic neurons in DAT-Cre mice, we showed that specific excitation of A11 dopaminergic neurons significantly increased head withdrawal thresholds in ipsilateral side (E), but not contralateral side (F), in the von Frey filament test and also increased the time spent in the paired dark room in the CPP test (G). (H–J) By pharmacological intervention, we showed that intra-Sp5C injection of a D1 antagonist (SCH23390) inhibited the CCI-ION-induced neuropathic pain and enhanced the analgesic effect of A11 dopaminergic neuronal excitation (H); however, intra-Sp5C injection of a D2 antagonist (spiperone) exacerbated the CCI-ION-induced neuropathic pain and completely blocked the A11 dopaminergic neuronal excitation-produced analgesic effect in the CCI-ION model (I). As a control, intra-Sp5C injection of saline (vehicle) had no significant effect (J). n = 5–6 mice per group. *P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding Baseline values; #P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding CCI group; @P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding “CCI+A11 excitation” group.
