Figure 3.
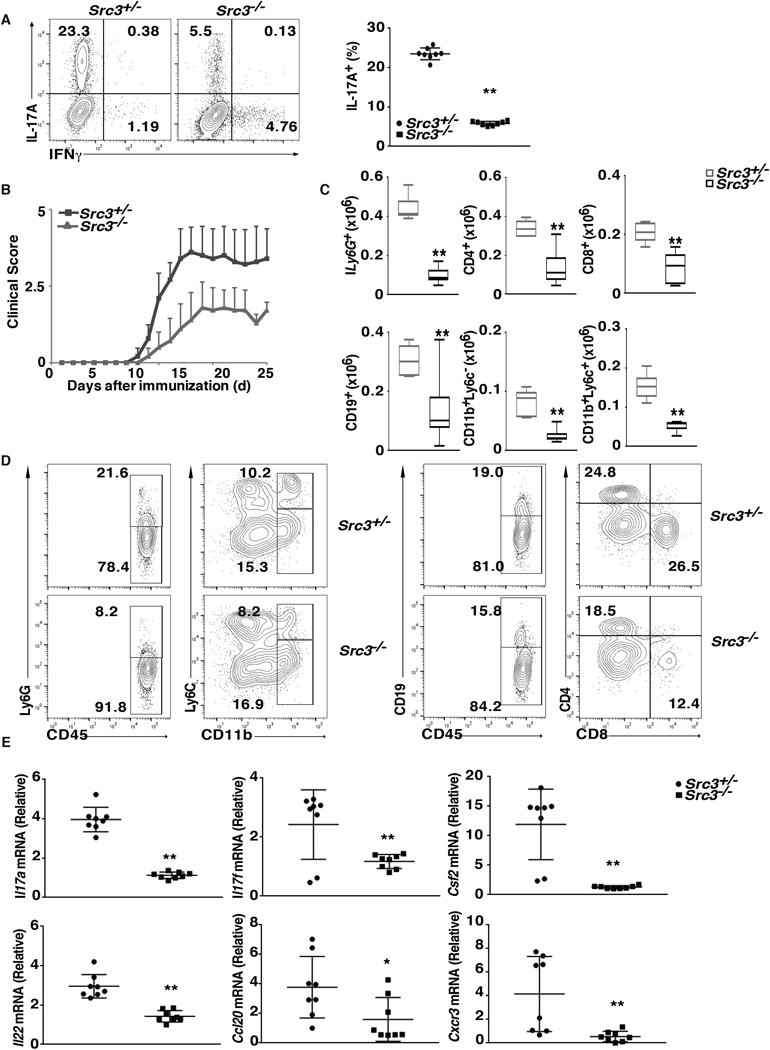
T cells from Src3−/− mice exhibit defective induction of EAE. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular IL-17A in naïve CD4+ T cells from Src3+/− and Src3−/− mice, cultured for three days under pathogenic Th17 priming conditions (TGFβ + IL-6 + IL-1 + IL-23) in vitro. Numbers in each plot indicate the percentage of the cells in the gated area. Right panels present the percentages of IL-17A+ cells from individual mice (n=7 per genotype). (B) Mean clinical EAE score of Src3+/− mice adoptively transferred with CD4+ T cells from MOG35–55-primed Src3+/− or Src3−/− mice (n = 5 per genotype) and further expanded in vitro for three days in the presence of MOG35–55 and IL-23 (20 ng/ml). (C) Quantification of cells expressing characteristic mononuclear cell surface markers among CNS-infiltrating cells in host mice adoptively transferred with Src3+/− or Src3−/− CD4+ T cells, assessed by flow cytometry at the peak of disease. (D) Gating strategy for lymphocytes shown in C. (E) qPCR analysis of Il17a, Il17f, Csf2, Il22, Cxcr3, and Ccl20 mRNA in lymphocytes that infiltrated the CNS of mice (as in B). Expression is presented relative to that of the control gene Actb. Data are from three experiments (A, right panel, and E, presented as mean ± SEM; C, presented as median [central line], the first and third quartiles [box ends], and maximum and minimum [extended lines]). * P < 0.05 (t-test); ** P <0.01 (t-test).
