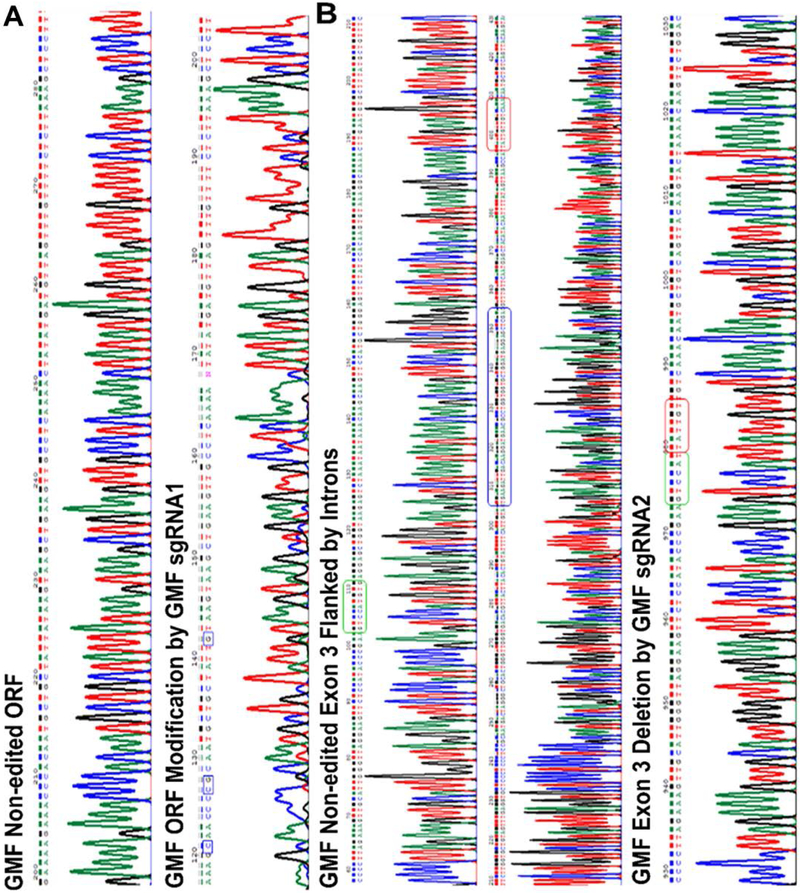
Figure 6A: SpCas9-mediated GMF editing leads to indels in GMF coding sequence:
a) The top panel shows the wild type GMF DNA sequence while the bottom panel shows the GMF edited sequence (using GMF-sgRNA1) from the exon 2 and is flanked by the intron sequences. GMF edited DNA sequence as a result of GMF sgRNA1-mediated editing leads to indels in the GMF coding sequence causing a frameshift in the GMF coding sequence. Specific nucleotide changes are indicated in the blue box, b) The top and the middle panels show the normal non-edited DNA sequence of the GMF exon 3 and the flanking introns. The bottom panel shows the deletion of GMF exon 3 post GMF gene editing. There is a significant change in the nucleotide sequence as a result of GMF gene editing. The green and the red boxes in the top and the middle panels depict the normal GMF DNA sequence. The GMF exon 3 is depicted within the blue box in the middle panel. As a result of GMF gene editing the GMF exon 3 and the flanking partial intronic sequences have been deleted and are represented as green and red boxes in the bottom panel.