FIGURE 4.
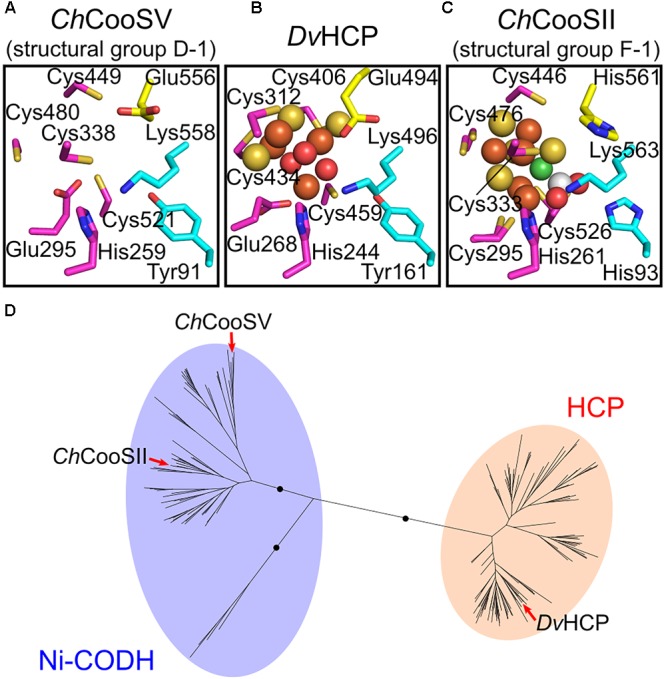
Structural and phylogenetic relationships of the catalytic sites between structural group D-1 Ni-CODHs and HCPs. (A) The predicted structure of the catalytic site of C. hydrogenoformans CooSV (structural group D-2; NCBI protein accession number: WP_011342982). (B) The structure of the catalytic site of D. vulgaris HCP (PDB ID: 1W9M). (C) The structure of the catalytic site of C. hydrogenoformans CooSII (structural group F-1; PDB ID: 4UDX). The residues forming the catalytic sites are represented in stick forms and colored as follows (related to Figure 2): magenta, the C-clusters and hybrid cluster; cyan, acid–base catalysts; and yellow, the Glu residue unique to the hybrid cluster of HCPs and the corresponding residues of C. hydrogenoformans CooSV and CooSII. The Ni, Fe, S, and O atoms of the metal clusters are colored in green, brown, yellow, and red, respectively. The C and O atoms of CO2 are colored in white and red, respectively. (D) The phylogenetic tree of the HCP family from the Pfam seed dataset (PF03063) (Finn et al., 2016). The branches of C. hydrogenoformans CooSII and CooSV and D. vulgaris HCP are indicated by red arrows.
