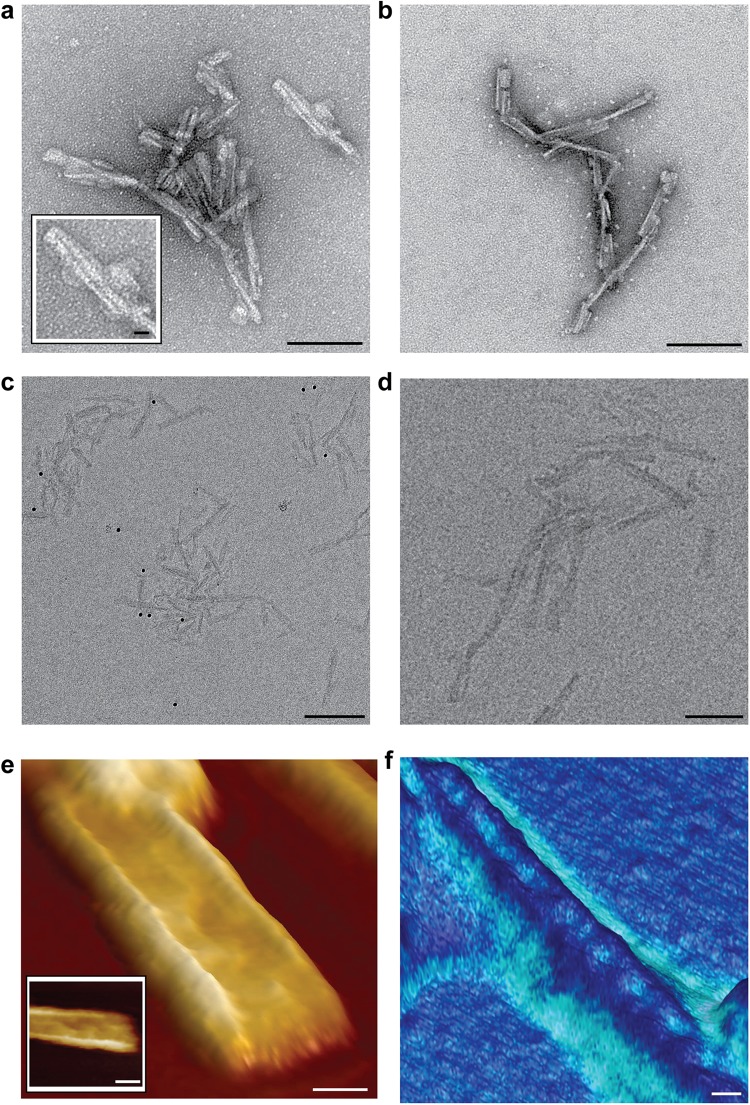
Figure 4.
Infectious RML prion rods imaged by negative stain EM, cryo-EM and AFM. (a,b) Negative stain EM images using (a) uranyl acetate at pH 4 and (b) NanoW at pH 6.8. (c,d) Cryo-EM images. (e) 140 nm × 140 nm AFM scan revealing the presence of material in the central gap of the rod which appears to link the paired fibres. Main panel 3D image, inset, 2D image. (f) AFM surface topography (height) adhesion force mode showing that material in the central gap region of the rod interacts more strongly with the scanning tip (exerts a greater adhesive force) than the rod fibres (light to dark representing high to low adhesive force). Scale bars, 100 nm main panels a, b and d, 200 nm panel c, 10 nm main panels e and f and insets in panels a and e.