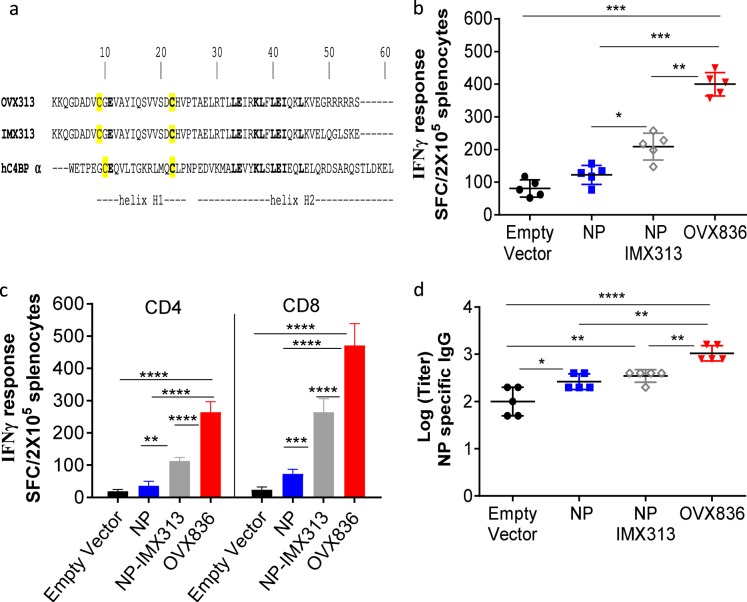
Fig. 1.
DNA-based immunization with nucleoprotein (NP) fused to a small oligomerization domain. a Primary structure of OVX313 oligomerization domain and alignment with IMX313 and the homologous human C4BP-alpha. Residues in bold type are identical. Cysteine residues are highlighted in yellow. b C57BL/6 mice were immunized with DNA plasmid encoding NP, NP-IMX313, OVX836 (NP-OVX313), or the empty vector by the intramuscular route. NP-specific interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-secreting cells were evaluated by ELISpot in splenic cells. The results represent the mean (line) and individual data points of each of the five mice with standard deviation of the mean (SD). c IFN-γ-secreting CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell, in the splenocytes stimulated with 5 µg/ml of NP protein or 5 µg/ml of NP366-374, respectively. d Serum anti-NP immunoglobulin G (IgG) were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Sera were individually tested in serial dilutions against purified NP protein. The mean (line) of each group is represented with SD. Levels of IgG are expressed as Log (endpoint dilution titer). Differences were assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test with 95% confidence interval, p < 0.05 is considered significant. The asterisks refer to the level of significance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). Results from a representative experiment of two performed are shown