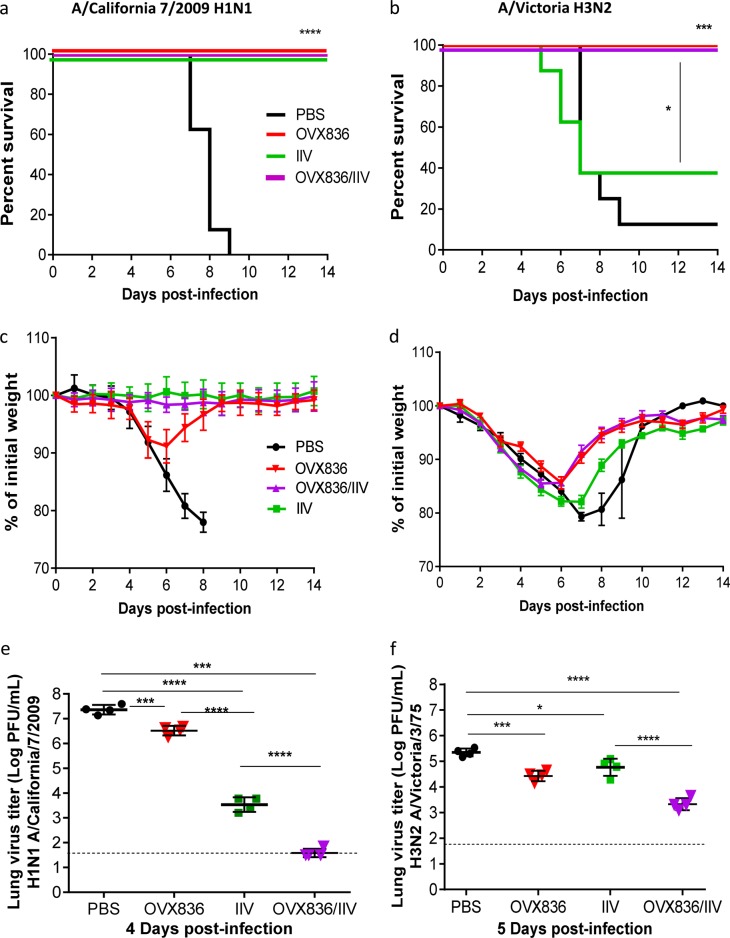
Fig. 5.
Vaccination with OVX836 induces broad protection against lethal challenge with different influenza A subtypes. Groups of 12 female Balb/c mice received two 21 days apart intramuscular (i.m.) immunizations with either PBS, inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV), OVX836, or a combination of IIV and OVX836 (OVX836/IIV). Three weeks after the second immunization, mice were intranasally (i.n.) infected with either 3LD50 of influenza H1N1 A/California/7/2009 (left panel) or 1LD50 of H3N2 A/Victoria/5/72 (right panel) virus. a, b Percent survival rates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 by log-rank (Mantel–Cox), c, d mean weight changes (±SEM), e, f mean lung viral titers expressed as log (PFU/mL ± SD) on day 4 or 5 post-infection. Individual virus titers are given and lines represent averages. In all, 1.7 log PFU/mL is the detection limit of the technique (dotted line). Statistical significance of the variance between multiple groups was calculated with Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001,****p < 0.0001)