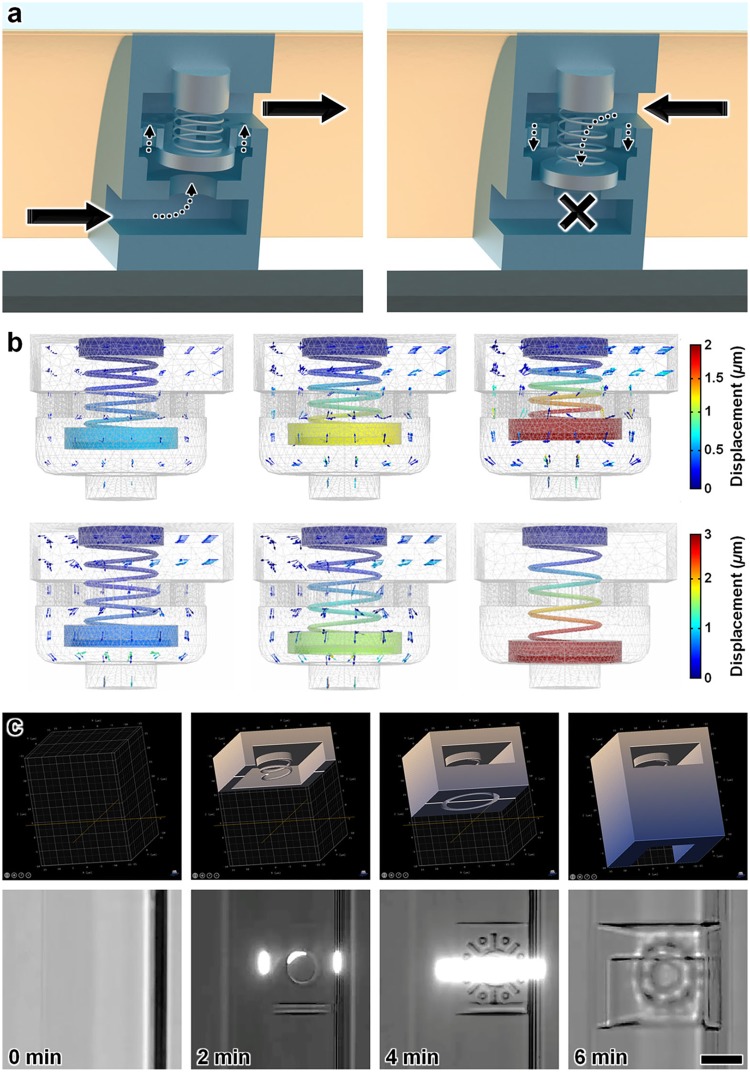
Figure 4.
IsDLW-based 3D microfluidic coil spring diode. (a) Conceptual illustrations of flow rectification functionality. (Left) Under forward flow conditions, the helical coil spring compresses as the sealing disc is directed away from the bottom orifice, thereby permitting fluid flow through the radially arrayed through-holes and then out the top orifice. (Right) Under reverse flow conditions, the helical coil spring expands as the blocking disc forms a fluidic seal at the bottom orifice, which physically obstructs the flow of fluid through the element. (b) Sequential COMSOL Multiphysics fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulations of flow dynamics corresponding to forward flow (Top) and reverse flow (Bottom) (see also Supplementary Movie S4). Arrows denote fluid velocity field vectors. (c) Sequential CAM simulations (Top) and corresponding isDLW fabrication results (Bottom) for printing a 3D microfluidic coil spring diode within a sol-gel-coated PDMS microchannel with a semi-ovular cross-sectional profile and height of ~25 μm (see also Supplementary Movie S5). Scale bar = 10 μm.