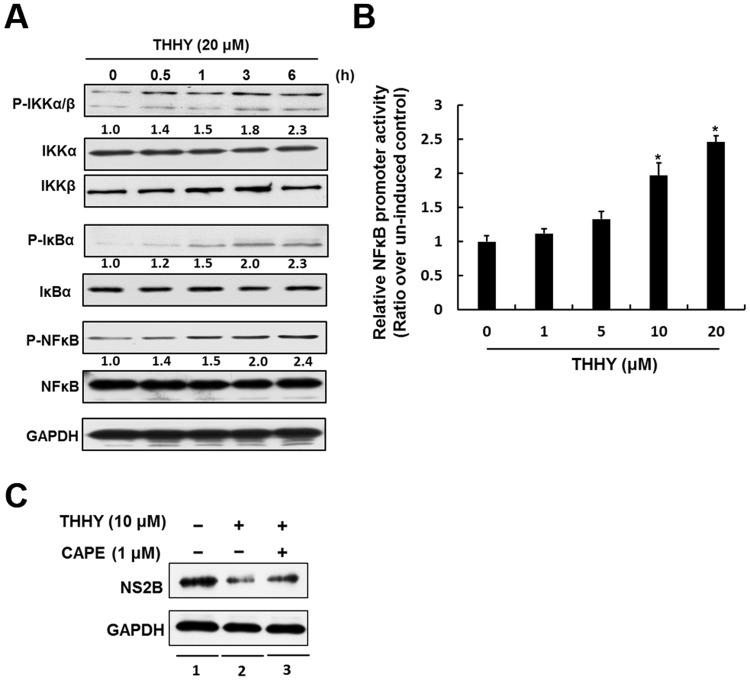
Figure 2.
THHY inhibits DENV replication via up-regulation of NF-κB activity. (A) THHY induces NF-κB activity upon DENV replication. Huh-7 cells were infected by DENV at an MOI of 0.2 and then treated with 20 μM THHY. Total cellular protein was harvest at 0,0.5,1,3, and 6 h post treatment. NF-κB (P-NFκB), IKK-α/β (P-IKKα/β), and IκBα (P-IκBα) phosphorylation were determined by western blotting with anti-phosphorylated NF-κB, IKK-α/β and IκBα antibodies, respectively. The total NF-κB (NFκB), IKK-α/β (IKKα and IKKβ) and IκBα (IκBα) levels were determined by western blotting with anti-NF-κB, IKK-α/β, and IκBα antibodies, respectively. (B) THHY induces NF-κB promoter activity upon DENV replication. Huh-7 cells were transiently expressed pNF-κB-Luc and then infected by DENV at an MOI of 0.2. After virus infection, cells were treated with THHY with indicated concentrations, and the luciferase activity was measured at day 3 post-treatment. (C) NF-κB specific inhibitor, CAPE, attenuates the anti-DENV effect of THHY. The DENV-infected Huh-7 cells were co-treated with 20 μM of THHY and 1 μM of CAPE for 3 days. Total cell lysates were harvested for analysis of DENV protein levels by western blotting. The treatment of 0.1% DMSO, marked “0”, was served as a negative control. Error bars represent the means ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n = 3). *P < 0.05.