FIGURE 1.
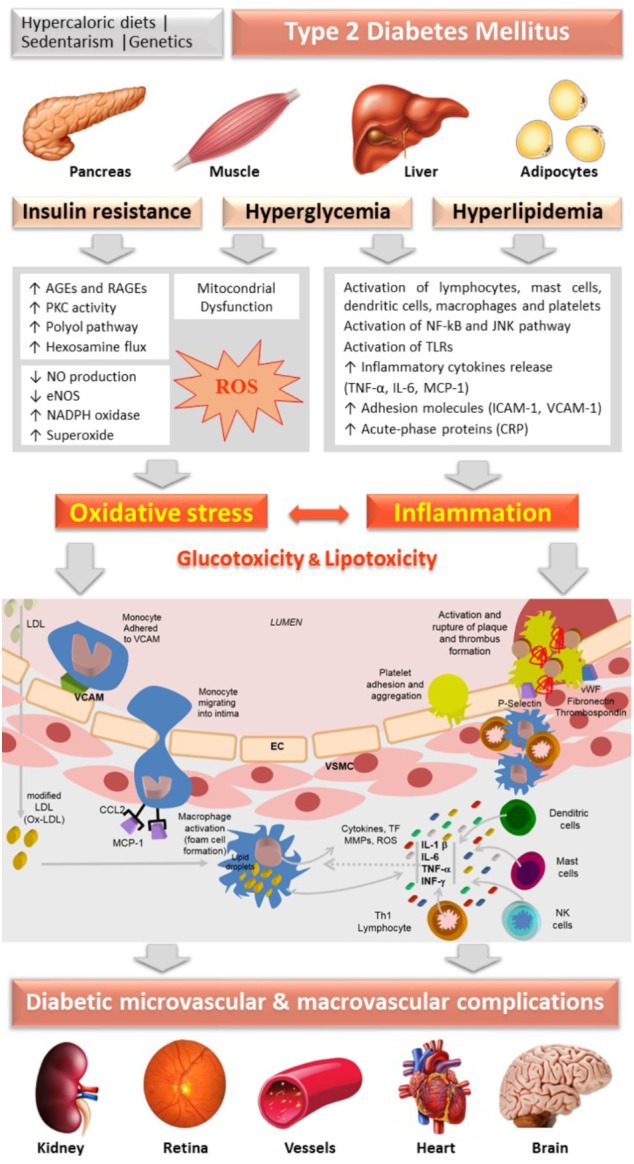
Schematic diagram representing the central role of oxidative stress and inflammation, guided by insulin resistance, hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia (gluco and lipo toxicity), in the vascular changes underlying the progression of micro and macrovascular complications of diabetes. AGEs, advanced glycation end products; CRP, C-reactive-protein; EC, endothelial cells; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ICAM-1, intracellular adhesion molecule-1; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; JNK, c-jun NH2-terminal kinase; LDL, Low Density Lipoprotein; MCP-1 (CCL-2), Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NO, nitric oxide; PKC, protein kinase C; RAGEs, receptor for AGEs; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR, Toll-Like Receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alfa; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cells; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
