Fig. 3.
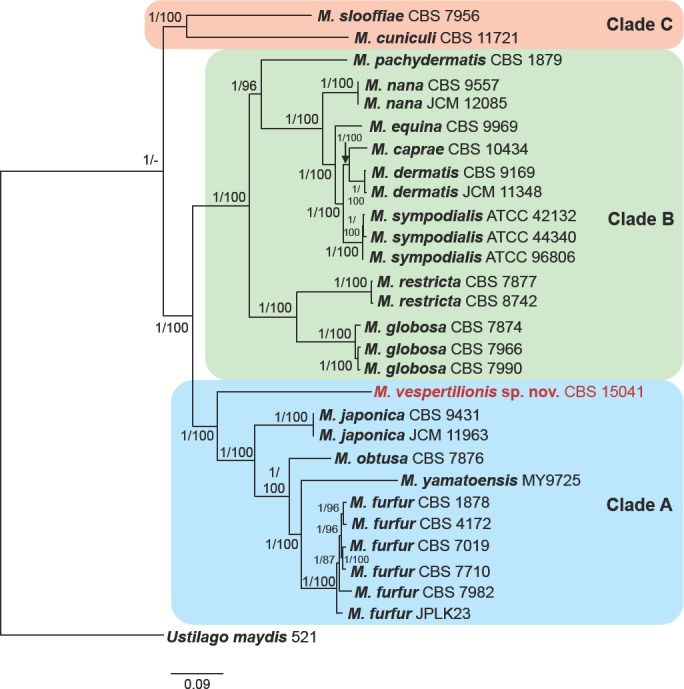
Phylogenetic tree of the genus Malassezia based on concatenated amino acid sequences of 254 conserved orthologues. The tree from the Bayesian analysis is shown, but the tree generated from the maximum likelihood analysis had an identical topology. Posterior probabilities (Bayesian)/bootstrap values (maximum likelihood), respectively, are shown at the nodes. Ustilago maydis was used to root the tree. Clades A, B, C as described by Wu et al. (2015) are illustrated. Based on the analyses, M. vespertilionis sp. nov. is a basal member of clade A.
