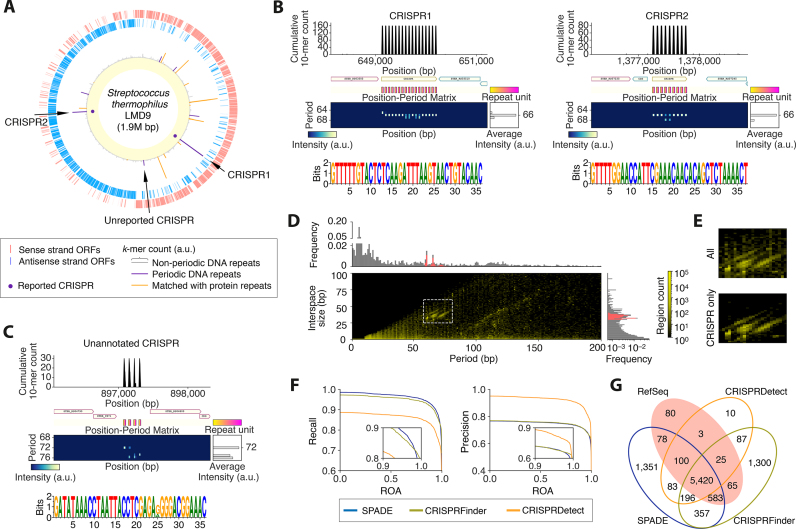
Figure 1.
CRISPRs detected by SPADE. (A) Circular genome map of the S. thermophilus LMD-9 genome. From the outer side, it represents genes encoded on the sense and antisense strands of the genome, cumulative k-mer counts with the annotations of periodic DNA and protein repeats, and the previously reported CRISPR loci. (B) Previously reported CRISPRs detected by SPADE. Each periodic repeat region is visualized along with cumulative k-mer count, neighboring genes, positions of repeat unit sequences and position-period matrix of the surrounding genomic region, and its motif sequence is represented by sequence logo. Each periodic repeat unit is represented by a gradient box where color indicates relative position in each repeat unit sequence. (C) A novel CRISPR found in the S. thermophilus LMD-9 genome. (D) Period-interspace size distribution of the entire periodic DNA repeats captured in the 7006 RefSeq prokaryotic genomes. Magenta bars in the probability density distributions represent CRISPRs reported in the RefSeq dataset. Dashed white line box represents DNA repeats further screened as CRISPR candidates. (E) Enlarged view of the dashed white line box in (D) and distribution of the RefSeq CRISPRs in the same area. (F) Precision and recall in predicting RefSeq CRISPRs by SPADE, CRISPRFinder and CRISPRDetect along with region overlap agreement (ROA) thresholds. (G) Venn diagram for DNA repeats detected by SPADE, CRISPRFinder and CRISPRDetect with ROA of ≥50% and their agreement with RefSeq CRISPRs.