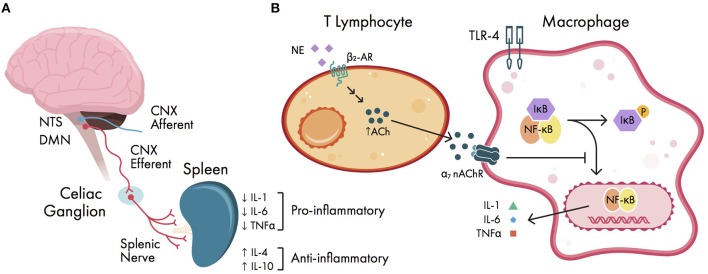
Figure 3.
Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. (A) schema of vagal reflex arc. Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are sensed by vagal afferents; the efferent vagal arc terminates in the celiac ganglion onto splenic nerve fibers, ultimately causing downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines. (B) cellular signaling within the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Splenic nerve endings terminate near T lymphocytes and increase acetylcholine (ACh) production via β2 adrenergic receptors (β2-ARs). The expressed ACh can activate circulating macrophages via alpha-7 nicotinic ACh receptors (α7 nAChRs). Activation of α7 nAChRs causes downstream inhibition of NF-kB activation, ultimately decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokine release. CNX, cranial nerve X (vagus nerve); DMN, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; IL, interleukin; NE, norepinephrine; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; P, phosphate group; TLR-4, Toll-like receptor 4; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha.