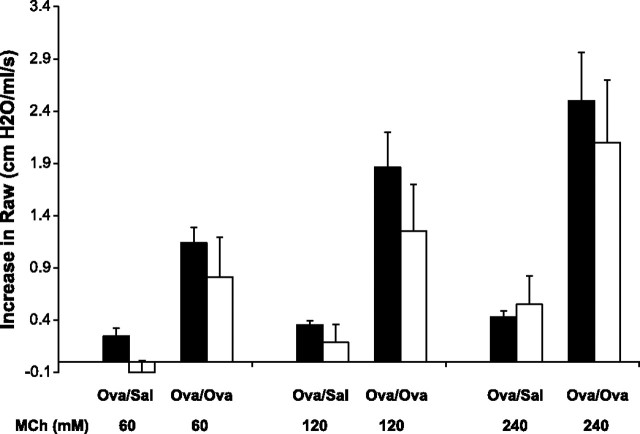
Fig. 1.
Increase in nasal resistance is similar in magnitude to the increase in pulmonary resistance. Methacholine (MCh)-induced increase in pulmonary and nasal airway resistance (mean ± SD, shaded and open bars, respectively), is shown for control mice (Ova/Sal, n = 10) and sensitized and challenged mice (Ova/Ova, n = 10).