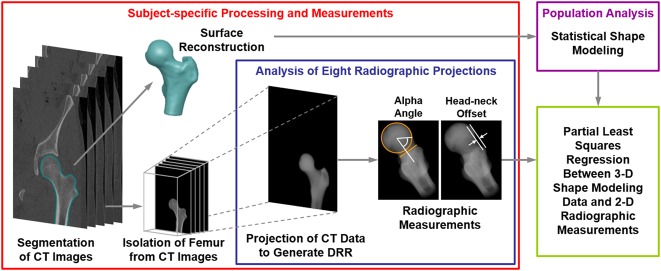
Fig. 1.
Flowchart shows the methodological pipeline that included SSM and analysis of radiographic measurements used to diagnose cam FAI. Both cam FAI and control group participants were considered. For each individual analyzed, CT images were segmented to isolate the proximal femur. Reconstructed surfaces were input to SSM. Digitally reconstructed radiographs were then generated to represent eight plain film views commonly obtained in patients with suspected cam FAI. The reconstructed radiographs were generated by projecting the CT image stack, including only the pixel intensities within the proximal femur, at fixed rotation angles (Table 1). Alpha angle and head-neck offset measurements were obtained on each digitally reconstructed radiograph. Partial least squares regression was performed between the radiographic measurements and shape score to determine which radiographic view(s) and associated α angle and head-neck offset measurements best described the 3-D shape score calculated by SSM. DRR = digitally reconstructed radiograph.