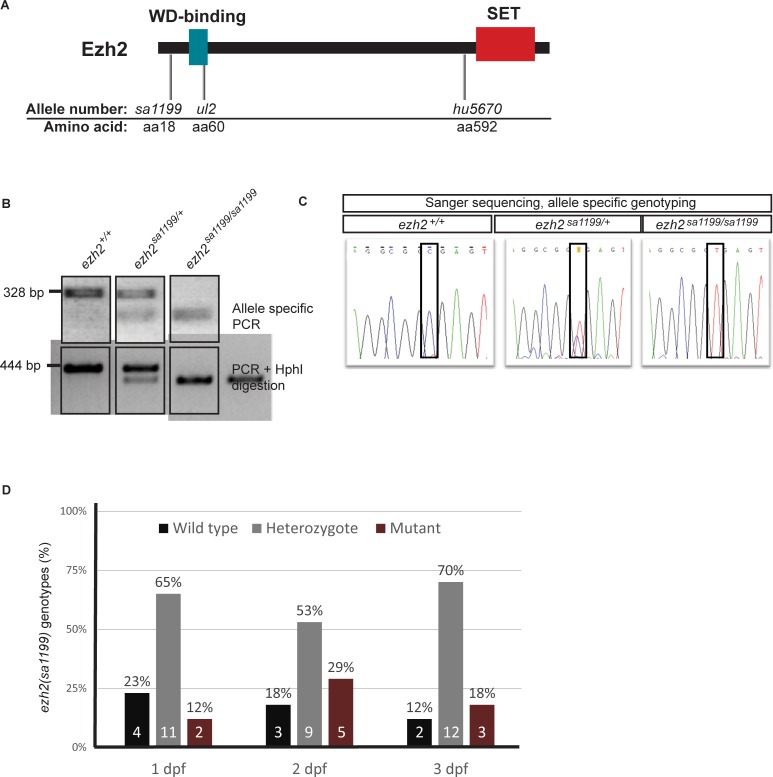
Fig 1. Validation of ezh2(sa1199) genotypes.
A. Ezh2, its domains, and mutant allele positions (grey lines). The green and red boxes indicate WD-binding and SET domains, respectively. The ezh2(sa1199) allele (left) has a stop mutation on the arginine 18 position (R18STOP), ezh2(ul2) allele (middle) has a 22 bp insertion that leads to a nonsense codon at amino acid 60, and ezh2(hu5670) allele (right) has a nonsense mutation on the arginine 592 (R592STOP) position. B. Allele specific (top) and PCR-restriction (bottom) genotyping on caudal fin clips of 2 dpf embryos. Agarose gel electrophoresis shows differential amplification or restriction enzyme digestion of the alleles. A wild type, heterozygous, and mutant genotype from a single experiment is represented for each method. C. Allele-specific genotyping validation by Sanger sequencing. Two dpf embryo fin clips were allele-specifically genotyped and Sanger-sequenced to validate the genotyping method. The mutation locus (black box) is visualized for wild type (left), heterozygous (middle), and mutant (right) embryos. D. Allele specific genotyping of 1, 2, and 3 dpf ezh2(sa1199) in-crossed embryos (N = 17 per day). The percentage of wild types (black), heterozygotes (grey), and mutants (brown) show a Mendelian ratio. The number of embryos is indicated inside the bars of the graph in white.