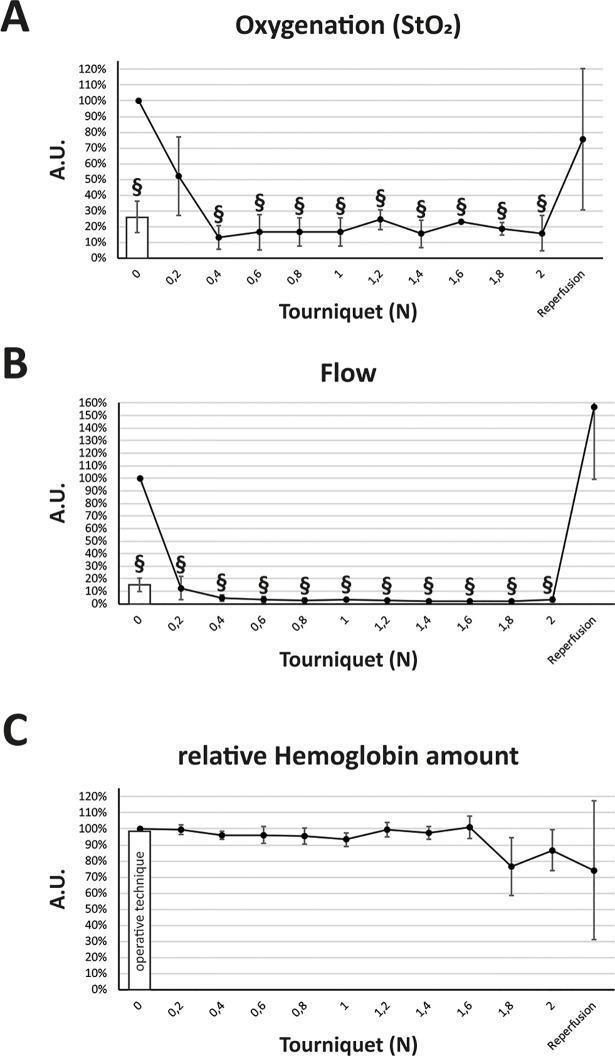
Fig 2. Microcirculatory measurement of oxygenation, flow and relative hemoglobin amount in the tourniquet and operative clamping model.
(A) Using the O2C device, relative oxygenation of the murine hind limb was significantly reduced at a force of 0.4 N with no further reduction by increasing pressure. The operative clamping model (bar) showed a significant reduction but not as high as the low-pressure tourniquet. (B) Microvascular flow was significantly decreased at a force of 0.2 N and upwards compared to the control as well as in the operative technique (bar). (C) The relative hemoglobin amount was not significantly changed by either the operative clamping technique or increasing tourniquet pressure. Results are shown as means ± SEM. P-value: # < 0.05; § < 0.001; (two sample t-test), n = 4.