Figure 2.
Nondiagnostic Feature Reduction and Diagnostic Feature Progression
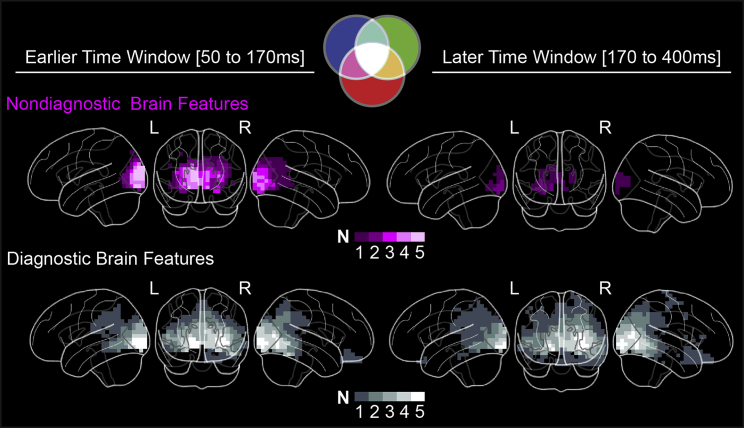
Magenta color-coded brains show voxels that represent at least one significant (FWER p < 0.05, one-tailed) nondiagnostic brain feature (represented with a magenta color in the Venn diagram) in earlier [50–170 ms] and later [170–400 ms] time windows post stimulus. White color-coded brains show voxels that represent at least one significant (FWER p < 0.05, one-tailed) diagnostic brain feature (represented with a white color in the Venn diagram) in earlier [50–170 ms] and later [170–400 ms] time windows post stimulus. Voxel brightness denotes the number (N) of observers for whom these criteria held true. For all observers, nondiagnostic features were consistently reduced over time in the occipital cortex while diagnostic features were sustained and progressed into the ventral pathway. See also Figure S2B. Abbreviations: left (L); right (R).