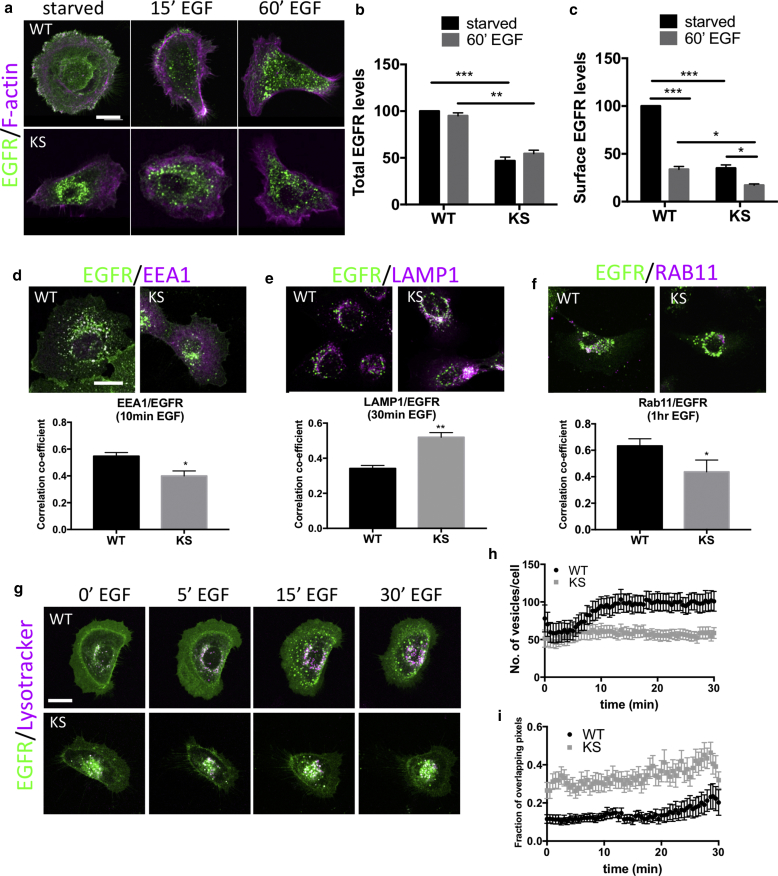
Figure 2.
EGFR localizes to lysosomal compartments in KS cells. (a) Immunostaining of EGFR (green) and F-actin (magenta) and (b) quantification of EGFR surface and (c) total levels from images in WT and KS cells after EGF stimulation. (d–f) Immunostaining and quantification of EGFR (green) localization with (d) EEA1, (e) LAMP1, or (f) Rab11a vesicles (all shown in magenta) after EGF stimulation (10 ng/ml). Graphs beneath images show Pearson correlation coefficient analysis of EGFR and specified compartments. N = 30 cells for each. (g) Still images from movies of WT and KS cells expressing EGFR-GFP labeled with LysoTracker Deep Red (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) (magenta) after EGF stimulation. (h) Quantification of the number of EGFR-positive vesicles and (i) EGFR/LysoTracker co-localization from WT and KS movies. N = 25 cells over three independent experiments. Data are all means ± standard error of the mean. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 using two-way analysis of variance (b and c) and t test (d–f). Scale bars = 10 μm throughout. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; hr, hour; KS, Kindler syndrome; min, minute; WT, wild type.