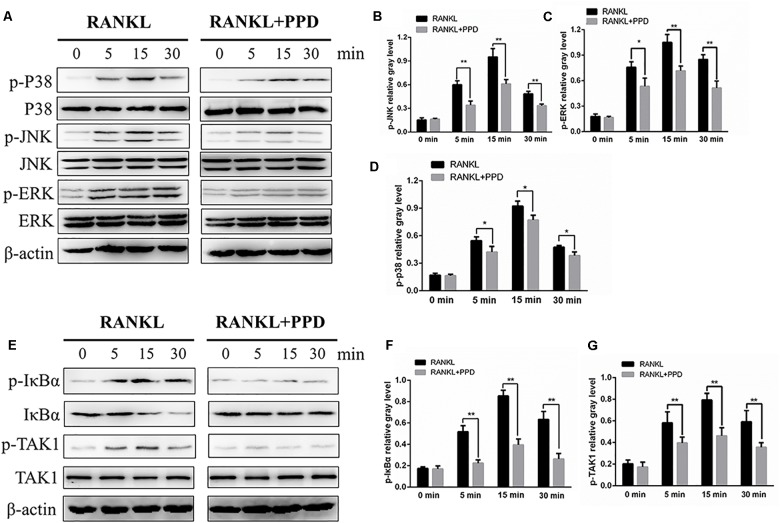
FIGURE 5.
PPD inhibited osteoclast differentiation by specifically impairing RANKL-induced MAPK cascades and the NF-κB pathway. (A,E) RAW264.7 cells were treated with or without 5 μM PPD for 2 h and then treated with 100 ng/mL RANKL for the indicated periods. Cell lysates were analyzed using western blotting with specific antibodies against phospho-p38, p38, phospho-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, phospho-JNK1/2, JNK1/2, phospho-IκBα, IκBα, phospho-TAK1, TAK1, and β-actin. (B–D) The gray levels corresponding to phosphorylation of the indicated proteins were quantified and normalized relative to β-actin using Image J for p-p38, p-JNK, and p-ERK, (F,G) The gray levels corresponding to phosphorylation of the indicated proteins were quantified and normalized relative to β-actin using Image J for p-TAK1 and p-IκBα. Significant differences between the groups were determined by paired Student’s t-test. ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 compared with the control group.