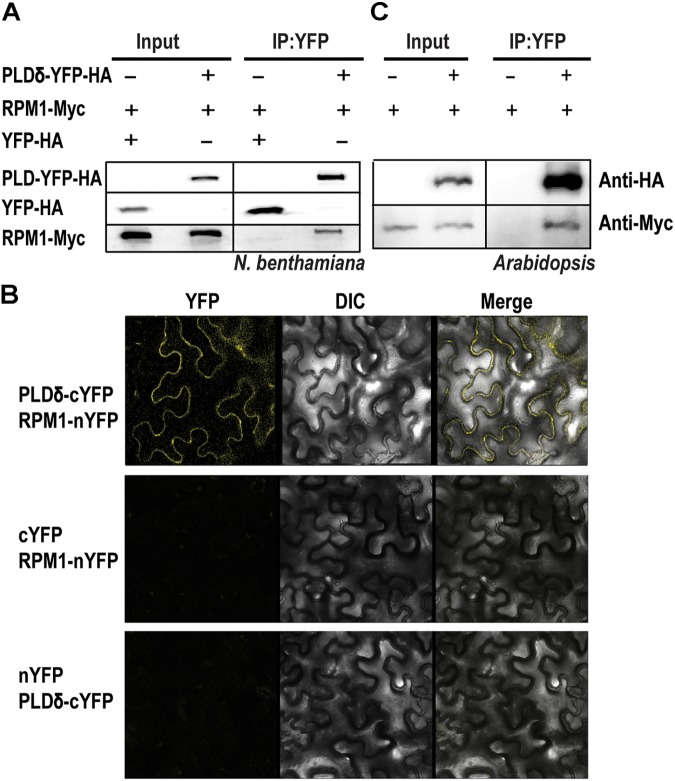
FIGURE 1.
PLDδ interacts with RPM1. (A) The interaction of PLDδ and RPM1 in Nicotiana benthamiana. 35S::PLDδ-YFP-HA and 35S::RPM1-Myc were co-expressed in the leaves of N. benthamiana. Total membrane proteins were extracted from samples collected at 2 days after infiltration. PLDδ-YFP-HA was immunoprecipitated with agarose beads conjugated with anti-GFP antibody, and RPM1-Myc was detected for Co-IP. Co-expression of 35S::YFP-HA and 35S::RPM1-Myc was used as the negative control. (B) Representative confocal images of BiFC. BiFC analysis was performed in N. benthamiana. PLDδ was fused with the C-terminal portion of YFP (cYFP), and RPM1 was fused to the N-terminal portion of YFP (nYFP). Different plasmids were co-expressed in N. benthamiana. Images were pictured at 2.5 days after infiltration. All the experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (C) The interaction of PLDδ and RPM1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Co-IP assay was performed with stable transgenic plants containing 35S::PLDδ-YFP-HA and pRPM1::RPM1-Myc. The transgenic plants containing pRPM1::RPM1-Myc was used as the negative control.