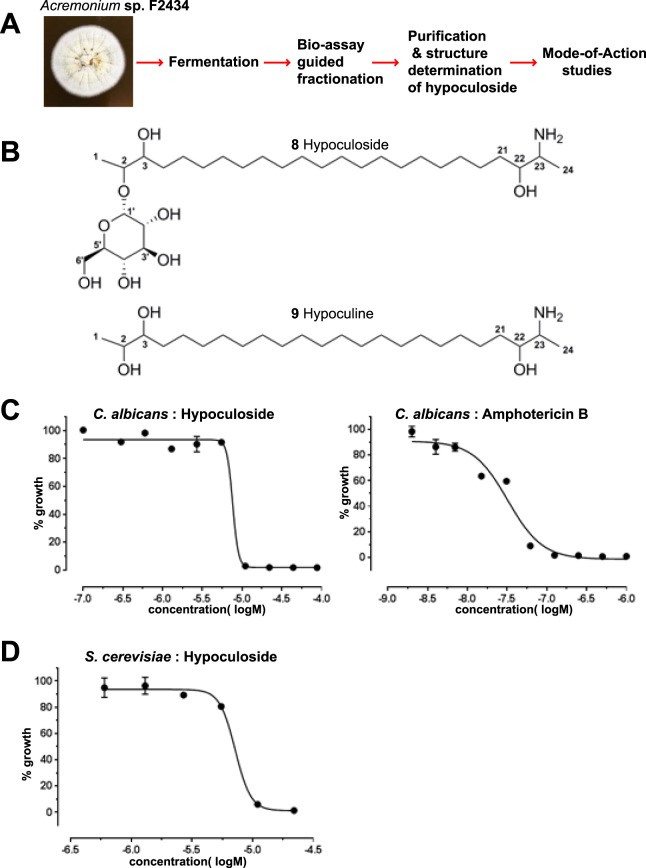
Figure 2.
Hypoculoside has antifungal activity. (A) Workflow used in the purification and analysis of hypoculoside from Acremonium sp. F2434. (B) Structure of hypoculoside (8) and its aglycone derivative hypoculine (9). (C) Logarithmically growing Candida albicans cells were exposed to hypoculoside and amphotericin B at various concentrations in triplicates in a 96-well microplate. Growth of the cells was quantified by recording the absorbance at 600 nm after 24 hours. Growth (normalized with respect to DMSO-treated cells) is plotted against log of concentration of the compound. A picture of the microplate after 24 hours of incubation at 30 °C is shown in Supplementary Fig. S2A. (D) Effect of hypoculoside on the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells grown in YPD medium was analyzed in the similar way as for Candida albicans described above in C.