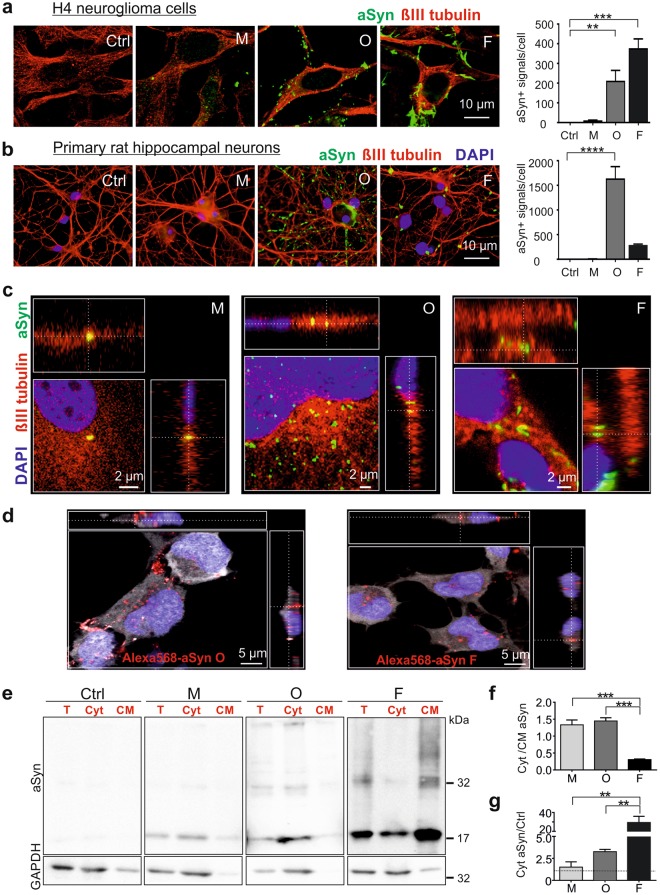
Figure 1.
Accumulation of extracellular aSyn species in recipient cells and uptake of extracellular aSyn. Cells were incubated either without aSyn (Ctrl) or with monomeric (M), oligomeric (O), and fibrillar (F) aSyn. (a,b) Representative fluorescent confocal images of H4 cells (a) and primary rat hippocampal neurons (b) labeled with βIII tubulin (red) and aSyn (green). Quantification of ICC (right) shows a stronger co-labeling of extracellularly added aggregated aSyn species with recipient cells. For quantification, the counts of aSyn immunopositive signal/cell were determined (n = 3, One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). (c) ICC and Z-stack images of aSyn-exposed H4 cells. Immunosignals of exogenous aSyn (green) were partly inside cells visualized by βIII tubulin (red). (d) ICC and Z-stack images of H4 cells exposed to AlexaFluor568-labeled aSyn oligomers (left) and fibrils (right). Labeled aSyn, βIII tubulin, and DAPI are present in red, white, and blue, respectively. (e) Representative WB images of exogenous aSyn in total cell homogenate (T), in the cytosol (Cyt), and in cellular membrane (CM) fraction of exposed H4 cells show the presence of exogenous aSyn in the cytosol. Lanes of aSyn and GAPDH within one frame (T, Cyt, and CM) are derived from the same blot. aSyn and GAPDH in T, Cyt, and CM fractions of each sample were probed in the identical blot. In each experiment, samples on different gels and blots were processed in parallel under same SDS-PAGE and immunodetection conditions, and exposed together for chemiluminescent detection. (f) Analysis of the proportion of aSyn distributed in cytosolic (Cyt) and associated with cellular membrane (CM) by calculating the ratio of aSyn levels in Cyt and CM fractions. (g) Relative aSyn levels in the cytosol of aSyn-exposed cells normalized to those of control cells (n = 3, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test).