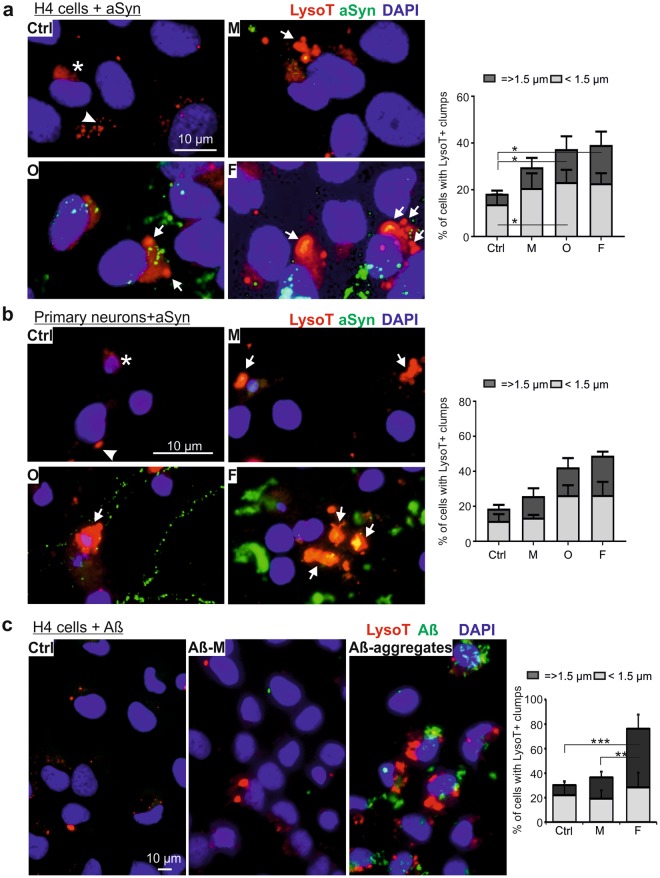
Figure 5.
Morphological changes in lysosomes of aSyn or Aβ-exposed cells. (a,b) H4 cells (a) and rat primary neurons (b) were exposed to monomeric (M), oligomeric (O), and fibrillar (F) aSyn. Lysosomes were probed with LysoT and their morphology was analyzed by fluorescent microscopy (left panels of (a,b)). In untreated cells (Ctrl), LysoT staining demonstrates diffuse (asterisks) or small puncta-like structures (arrowheads). In both H4 cells and primary neurons, extracellular administration of aSyn induces a pronounced enlargement of lysosomes characterized by the formation of LysoT+ clumps (arrows). The proportion of cells carrying larger LysoT+ clumps (diameters = >1.5 µm) enhances in aSyn-exposed cells with increasing aggregation states of extracellularly applied aSyn. (c) Enlargement of lysosomes probed by LysoT (red) in H4 cells treated with 1 µM Aβ monomers (Aβ-M) and aggregates for 24 h (ICC: left; quantification: right). Quantification for (a–c), n = 3, Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.