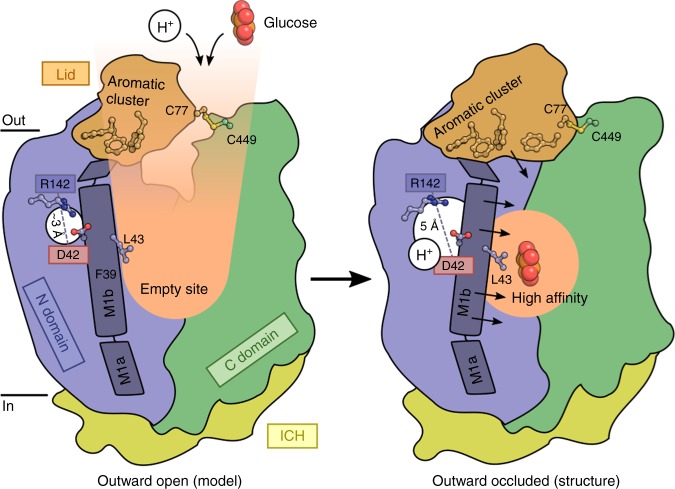
Fig. 4.
Proposed mechanism of glucose coupling to proton donor/acceptor site. In the outward open conformation (left), protons and glucose enter the central binding sites through small rearrangements of the N domain and the Lid domain that is covalently linked to the C domain through Cys77-Cys449. Protonation of Asp42 leads to its repulsion away from Arg142 and pushes the flexible M1b towards the glucose binding site, giving preference to high affinity glucose binding through Phe39 and Leu43 (right, observed structure). The aromatic cluster of the lid helps to isolate the proton donor/acceptor pair and maintain pKa values of Asp42 conductive to transport at a broad range of pH values