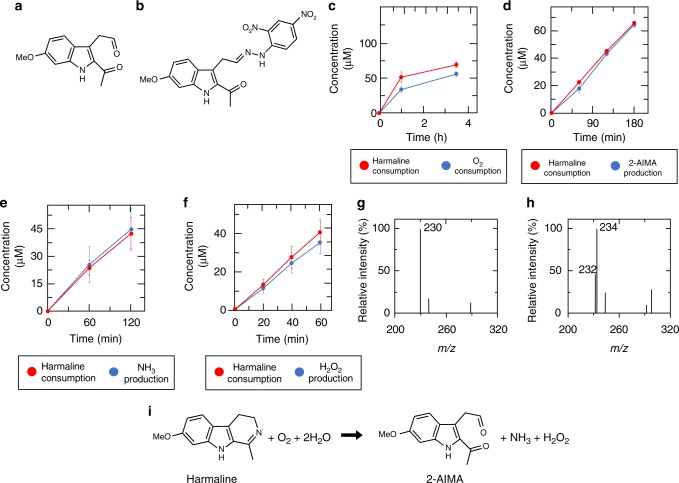
Fig. 2.
Identification of the reaction formula of HarA-catalyzed reaction. The reaction products and the stoichiometry of HarA-catalyzed harmaline degradation were determined. Structures of 2-AIMA and DNPH-derivatized 2-AIMA are shown in a and b, respectively. Each of consumption of c O2 and productions of d 2-AIMA, e NH3, and f H2O2 were measured. They are plotted in each panel together with the amounts of consumed harmaline during the reaction under the same conditions. All the assays were performed independently under the conditions in which reaction times and enzyme concentrations were optimized for each of the detection methods. All the assays were conducted in triplicate, and all data points represent the mean values ± S.D. for three experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. MS spectra of 2-AIMA which were synthesized in 100% H216O or 90% H218O/10% H216O are shown in g and h, respectively. i The reaction formula for HarA-catalyzed harmaline degradation. Two oxygen atoms of H2O2 are derived from O2