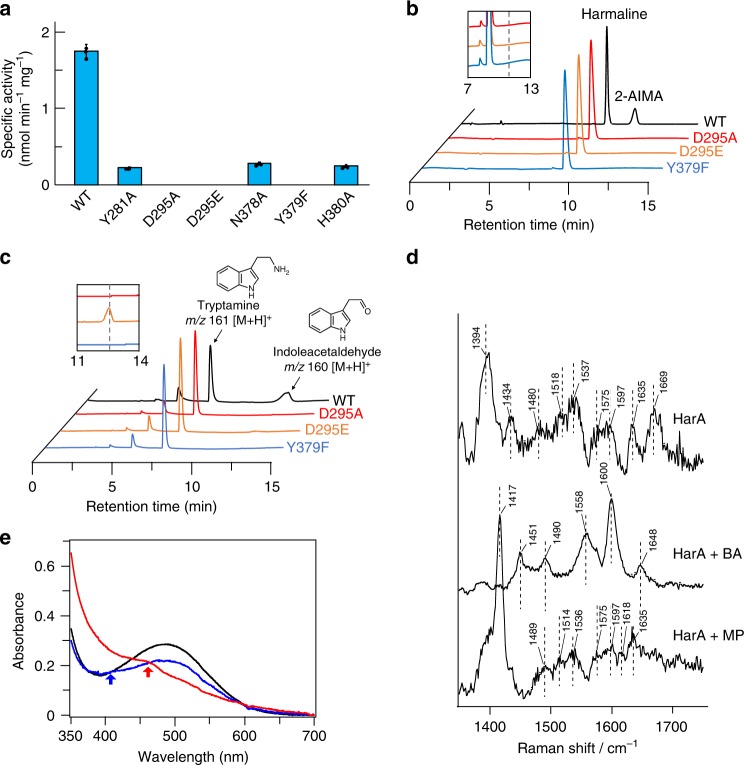
Fig. 5.
Identification of catalytic residues and reaction intermediates of HarA-catalyzed reaction. To obtain insight into the reaction mechanism of HatA-catalyzed cyclic imine cleavage reaction, various biochemical analyses were performed. a Specific activities of HarA mutants. All data points represent the mean values ± S.D. for three experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The reaction mixtures containing each of wild-type HarA, and the D295A, D295E and Y379F mutants were incubated with each of b harmaline and c tryptamine, and analyzed by LC/MS. Insets: magnified chromatograms (×10) of the three mutant enzymes. Dashed lines indicate the retention time in which each of the reaction products is detected. d Raman spectra of HarA without a substrate and with each of benzylamine (BA) and methylenepiperidine (MP) are shown. All spectra were obtained by subtracting the spectra of the Y379F mutant from those of native HarA. e UV-vis spectra of HarA were obtained with a spectrophotometer with an amine or imine substrate in an anaerobic environment. HarA was added to the reaction mixture containing 13 equivalents of benzylamine (blue), 5 equivalents of 2-methylenepiperidine (red), or 1% dimethylsulfoxide (black). Arrows indicate the peaks that appeared upon the addition of each substrate