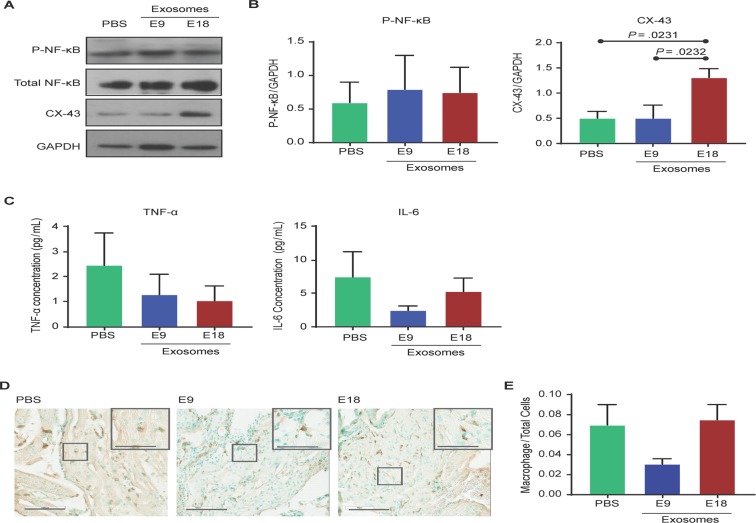
Figure 7.
Exosomes injected into pregnant mice induce labor-associated changes in the uterus. (A–C) Western blot and densitometry quantitation of NF-κB activation (as determined by RelA phosphorylation) and connexin-43 (CX-43) expression show that NF-κB activation is not significantly different between treatments, while CX-43 expression is significantly increased in E18 exosome-injected mice compared to PBS- or E9 exosome-injected mice. Inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α were not significantly increased in E18 exosome-injected mice compared to PBS- and E9 exosome-injected mice. Full-length blots are presented in Supplemental Fig. 4. (D,E) Histology showing that macrophage activation marker F4/80 was not significantly different regardless of treatment. Nuclei were stained green using methyl green and macrophages were stained brown. Total cells and macrophages were counted to determine macrophage to total cell ratio (bar graph).