Figure 1.
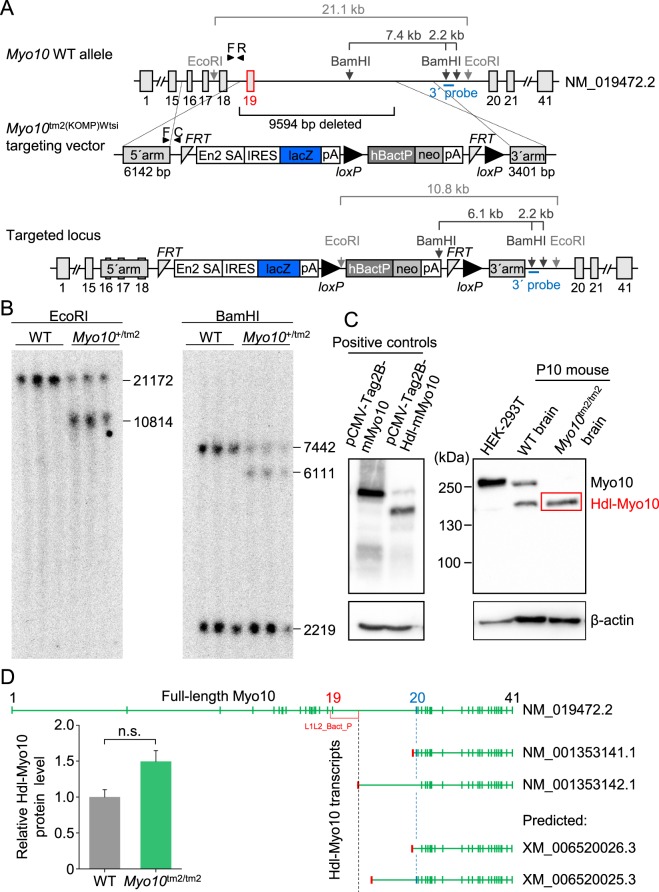
Myo10 reporter knockout (Myo10tm2/tm2) mice lack full-length (motorized) Myo10, but express the brain-specific headless isoform. (A) Schematic diagram showing the reporter knockout (tm2) targeting strategy. Insertion of the targeting sequence by homologous recombination causes loss of 9594 bp, including exon 19 and part of intron 19. Notably, the headless Myo10 isoform begins at exon 20. The gene trap, polyadenylation (pA) signal, is harbored in the IRES:lacZ cassette (IRES stands for internal ribosome entry site). (B) Southern blot analysis. DNA was fragmented using the restriction enzyme EcoRI or BamHI. The position of the radiolabeled hybridization probe at the 3′-end is indicated. Labeled DNA fragments were detected using X-ray film. (C) Western blot analysis. Lysates of HEK293T cells overexpressing full-length mouse (m) Myo10 (plasmid, pCMV-Tag2B-mMyo10) or headless (Hdl) mouse Myo10 (plasmid, pCMV-Tag2B-Hdl-mMyo10) were used as positive controls (blot on the left). Whole brain lysates obtained from P10 mice were used to screen for expression of full-length and Hdl-Myo10 (blot on the right). (D) Level of Hdl-Myo10 protein expressed in Myo10tm2/tm2 mouse brain (n = 3) relative to wild-type (WT) brains (n = 3), and mouse Hdl-Myo10 transcripts obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), National Institutes of Health (NIH). The accession prefix NM_ denotes confirmed protein-coding transcripts, whereas the prefix XM_ indicates predicted protein transcripts. Green (vertical) bars are exons (ranging from 1 to 41; indicated above) and red bars are 5′-UTRs (5′ untranslated regions), preceding the coding sequence. Notably, the 5′-UTR of Hdl-Myo10 transcript NM_001353142.1, which lacks exon 20 (labeled blue) and exon 21, is disrupted by insertion of the cassette (L1L2_Bact_P) used to generate the Myo10tm2 allele.