Figure 8.
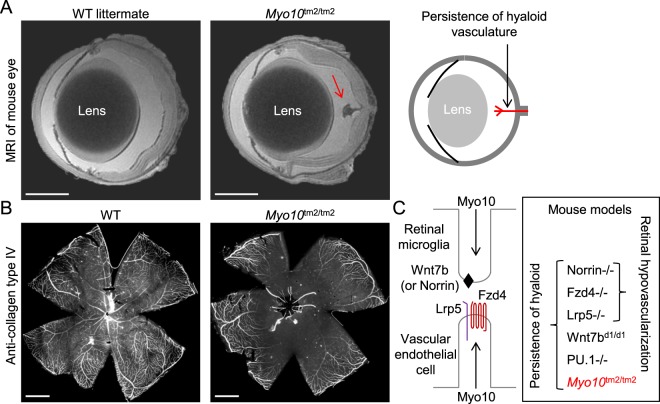
High penetrance of persistence of the hyaloid vasculature, without retinal hypovascularization, in Myo10tm2/tm2 mice. (A) High-resolution MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of enucleated and fixed eyes from adult wild-type (WT) and Myo10tm2/tm2 mice (representative of 6 eye scans for each genotype) reveals persistence of the hyaloid vasculature in mutant mice. The hyaloid artery emerges from the optic disc and extends towards the lens, as schematically illustrated on the right. Scale bars: 1 mm. (B) Whole-mount retina from an adult WT and Myo10tm2/tm2 mouse stained with anti-collagen, type IV antibodies. Hyaloid vessels can be seen emerging from the central optic disc of the Myo10tm2/tm2 retina. Scale bar: 1 mm. (C) Schematic diagram showing putative roles of Myo10 in macrophage-to-endothelial cell Wnt signaling, and knockout mouse models in which hyaloid persistence phenotypes, with or without retinal hypovascularization, manifest. Notably, Wnt7bd1 is a hypomorphic allele, implying that there is reduced, but not absent, Wnt7b gene function in Wnt7bd1/d1 mice. PU.1 null (PU.1−/−) mice lack macrophages.