Fig. 3.
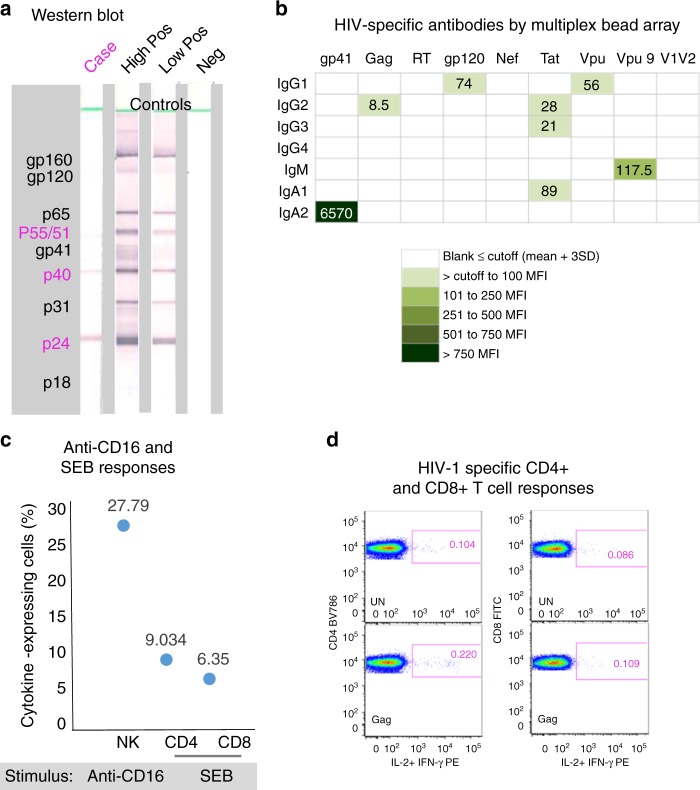
HIV-specific responses and immune response capability of the case at 9.5 years of age. a Detection of HIV-specific antibodies at 9.5 years of age by western blot. The case antibody profile is compared with controls that are a high positive, low positive and HIV-negative. HIV proteins corresponding to bands in the blots are shown in the left grey-shaded block; the case profile was positive for the core proteins indicated in pink. b Quantitation of HIV-specific antibodies by multiplex bead array for all isotypes and subclasses (indicated on the left side—IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgM, IgA1, IgA2) against gp41, Gag, RT, gp120, Nef, Tat, Vpu, peptide Vpu9 and V1V2 scaffold antigens (indicated at the top). Results are expressed as mean fluorescence intensities (MFI)), the colour key shows ranges of MFI according to colour intensity (the darker the more HIV-specific antibody detected). A result is considered positive if above the cut-off (mean ± 3 SD) determined from eight adult uninfected controls. Vpu9 amino acid sequence: STMVDMGHLRLLDVNDL. c Proportions of natural killer (NK) cells that respond to anti-CD16 antibody, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that respond to staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) in a whole blood intracellular cytokine (ICC) assay that measures induction of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-2 (IL-2). HIV-uninfected adult reference values for comparison (n = 21; median % and range)—natural killer (NK) anti-CD16%: 37.92 (12–67.6), CD4 SEB%: 6.04 (0.25–11.91), CD8 SEB%: 5.82 (0.18–18.94). d A weak positive CD4+ T cell response to Gag (0.116%) in the absence of a detectable CD8+ T cell response to Gag (<0.1%; 0.023%). UN: addition of costimulatory antibodies anti-CD28 and anti-CD49d, no stimulation with peptides