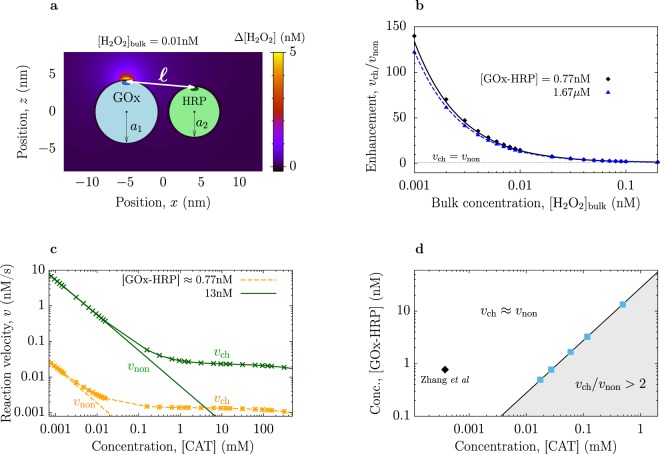
Figure 1.
Effect of proximity channeling on GOx-HRP cascade. (a) A model of a GOx-HRP complex and the distribution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, intermediate of the GOx-HRP cascade) shown as a deviation from the bulk concentration, Δ[H2O2] = [H2O2] − [H2O2]bulk. (b) Enhancement vch/vnon due to proximity channeling as a function of the bulk concentration of hydrogen peroxide. Symbols show the results of the full numerical calculations and the lines have been obtained using equation (1). (c) Reaction velocities of the channeled (symbols) and non-channeled (lines) reactions as functions of concentration of catalase (enzyme competing with HRP for hydrogen peroxide). (d) Channeling diagram showing the region where the enzyme proximity can at least double the reaction velocity. The diagram is drawn in the plane of the concentration of enzyme complexes and the concentration of catalase. We have assumed that [GOx-HRP] is the same as [GOx] = [HRP] in the non-channeled system. Squares show the results of the full numerical calculations and the line has been obtained using equation (3). The diamond shows the system with the maximal concentration of catalase studied experimentally by Zhang et al.34.