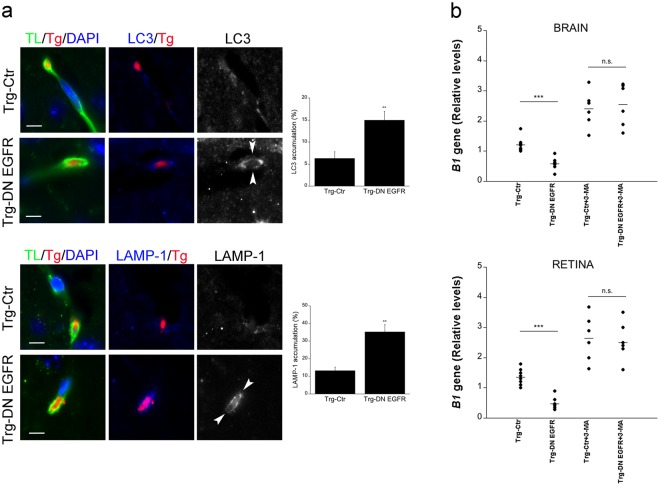
Figure 7.
In vivo accumulation of LC3 and LAMP-1 around T. gondii in brain endothelial cells and effects of administration of an inhibitor of autophagy on hematogenous invasion of the brain and eye by T. gondii. (a) Mice received T. gondii-infected dendritic cells i.v. After 18 h, mice were perfused and brain sections were stained with Tomato lectin-DyLight 488, anti-T. gondii Ab plus Alexa 568-conjugated secondary Ab and anti-LC3 or anti-LAMP-1 Abs plus Alexa 647-conjugated secondary Abs. Images to the left show parasites present in Tomato lectin+ cells (endothelial cells). The images from the Trg-Ctr mouse show a parasite not surrounded by accumulation of LC3 or LAMP-1. Ring-like accumulation of LC3 or LAMP-1 around parasite (arrowheads) is noted in images from the Trg-DN EGFR mouse (X630). Bar, 5 μm. Bar graphs represent percentages of parasites present in endothelial cells that were surrounded by accumulation of LC3 or LAMP-1 (mean ± SEM from 2 pooled experiments). **p < 0.01 (Student’s t test). (b) Mice that received T. gondii-infected dendritic cells i.v were treated with the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyl adenine (3-MA) or vehicle as described in Methods. Brains and retinas were obtained 1 d after i.v. challenge. Expression of B1 gene was assessed by qPCR. Levels were compared to those of one vehicle-treated Trg-Ctr mouse that was given an arbitrary value of 1. Results are pooled from 2 experiments. ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA).