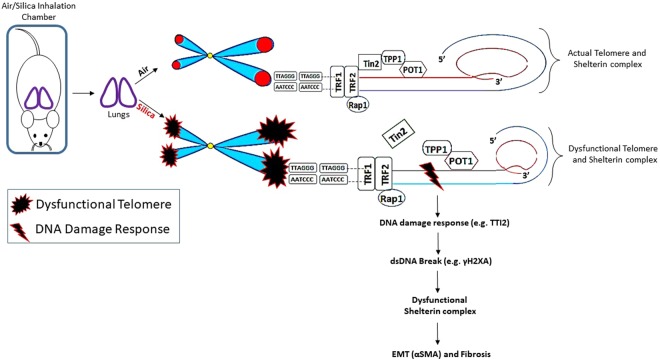
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the initiation of pulmonary fibrosis after silica inhalation is associated with shelterin dysregulation and dsDNA break in rat lung that may lead to a persistent and severe DDR (TTI2) at telomeres characterized by increased γH2AX and αSMA. Silica inhalation caused an increased staining in the number of γH2AX positive cells and an elevated αSMA expression in lung tissue compared to air control. Initiation of shelterin dysregulation was started after 3 wk of silica exposure as shown by the disruption of Tin2-TPP1 and remained persistent at 6 and 12 wk of silica exposure.