Figure 5.
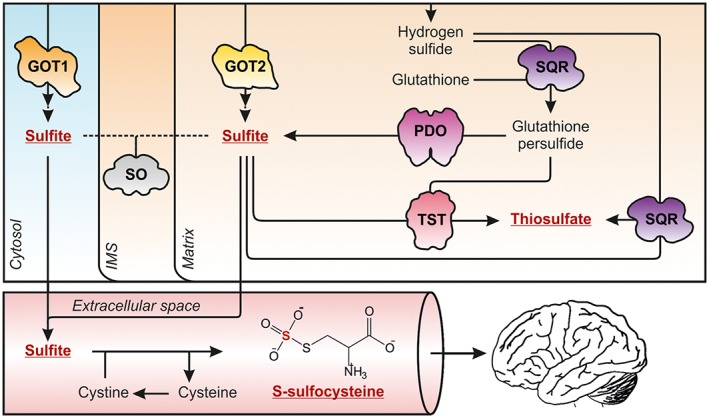
Sulfite excess facilitates the production of S‐sulfonates and causes brain damage. Missing SO activity results in the accumulation of cytotoxic sulfite, which diffuses out of the cell into the blood stream where it reduces disulfide bridges to form S‐sulfonates. S‐sulfocysteine (SSC) is the product of sulfite‐dependent cleavage of cystine. Within the brain, SSC is – like its structural homologue glutamate – excitotoxic. To what extent SSC can cross the blood–brain‐barrier or is formed in the brain is currently unknown. Under sulfite excess, an alternative reaction of SQR with H2S and sulfite leads to the formation thiosulfate. GOT1/2, 3II0/5AX8; PDO, 4CHL; SQR, 3H8L; SO, 1SOX; TST, 1RHD.
