Figure 1.
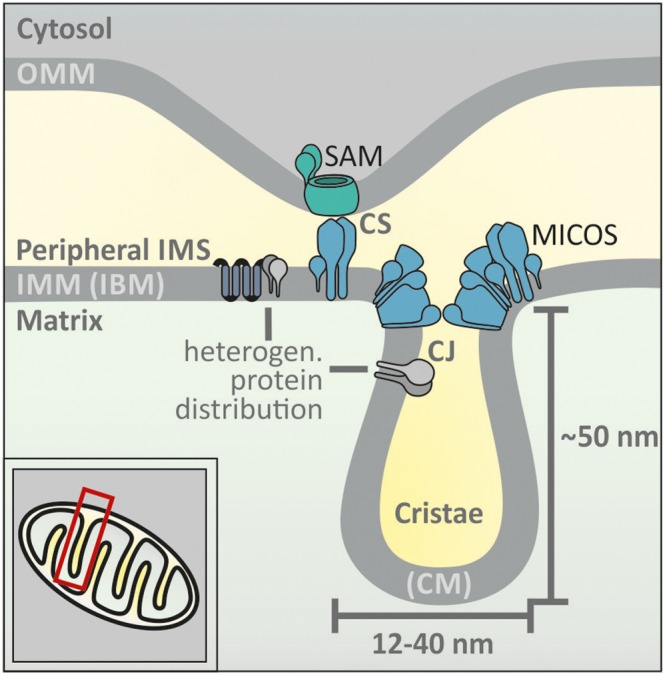
The layout of the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Mitochondria contain four sub‐compartments: the matrix, the OMM and IMM and the IMS. The IMS is subdivided into a peripheral IMS and cristae. The peripheral IMS is in contact with the OMM and the IBM. The cristae are enclosed by invaginations of the IMM and the CM. CJ segregate cristae and peripheral IMS. Contact sites (CS) formed by parts of the MICOS complex and the sorting and assembly machinery (SAM) complex mediate contacts between OMM and IBM. The OMM contains few proteins that have a high mobility in the membrane. Conversely, IMM proteins are more restricted in their movement. The structure of the IMM leads to heterogeneous protein distribution, for example, different protein sets between IBM and CM.
