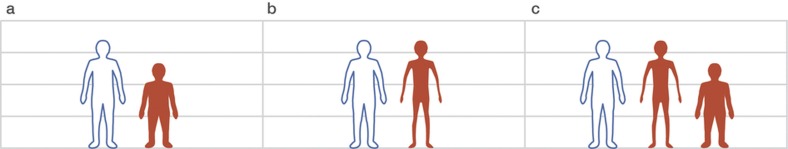
Figure 1. Measurement of child growth failure.
a, Stunting is a manifestation of chronic malnutrition and is defined as a height-for-age z score (HAZ) that is two or more standard deviations (s.d.) below the reference median. b, Wasting is an emaciated state resulting from acute malnutrition and is defined a weight-for-height z score (WHZ) of <−2. c, Underweight is a weight-for-age z score (WAZ) of <−2 and is considered a marker of subacute malnutrition, but is nonspecific from an anthropometric standpoint, because it can indicate either low weight for height, low height for age or some combination of both. There are multiple permutations of child growth failure and the silhouettes are simply illustrative of what a stunted, wasted or underweight child may look like. The World Health Organization Global Targets 2025 to improve maternal, infant and young child nutrition call for a 40% reduction in stunting and a reduction and maintenance of child wasting to less than 5% in children under five. While there is no target for child underweight, a reduction of 40% was used in this analysis.