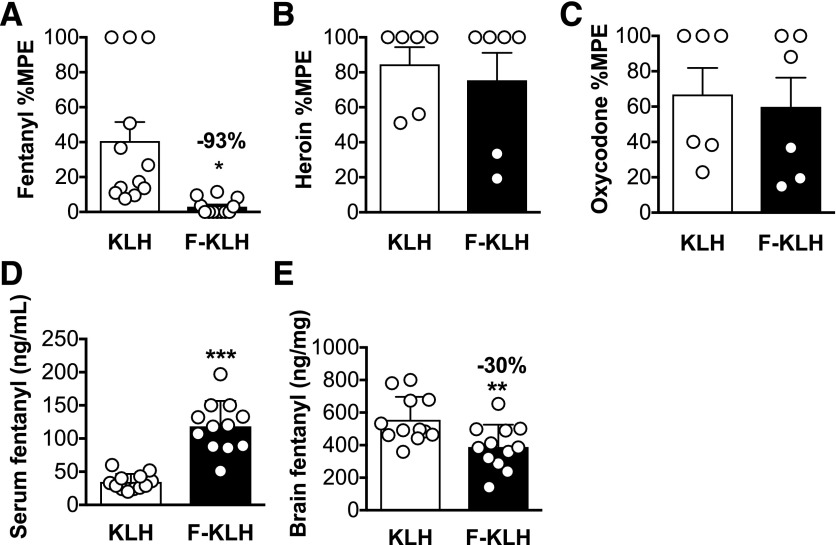
Fig. 3.
Experiment 2. Selectivity and pharmacokinetic efficacy of F-KLH in rats. (A) Vaccination with F-KLH significantly reduced fentanyl-induced hotplate antinociception by 93% 30 minutes after a 0.035 mg/kg, s.c., dose of fentanyl. (B and C) F-KLH had no effect on heroin- or oxycodone-induced antinociception 30 minutes after a 1 or 2.25 mg/kg dose of heroin or oxycodone, respectively. Serum fentanyl concentrations were significantly increased (D) and brain fentanyl concentrations were significantly decreased (E) compared with controls 4 minutes after a 1-minute 0.05 mg/kg, i.v., infusion of fentanyl. Numbers above bars represent the percentage difference from controls. *P < 0.05; - *P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared with controls. Mean ± S.D. (D and E), mean ± S.E.M. (A–C); n = 12/group (A, D, and E) and n = 6/group (B and C).