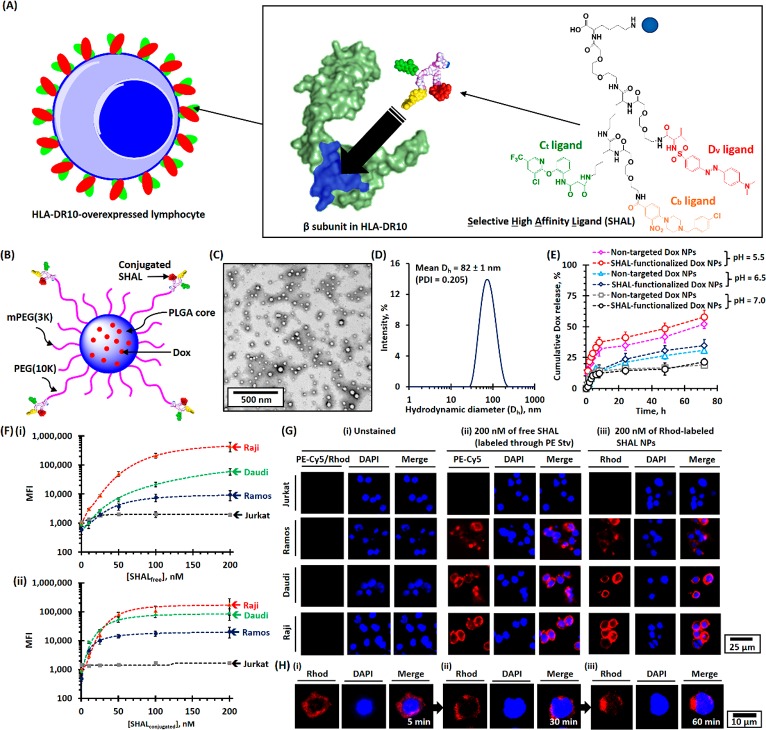
Figure 1.
Physicochemical properties of SHAL-functionalized Dox-encapsulated PEG-PLGA NPs. (A) Schematic of the binding of SHAL to the Lym-1 binding pocket in the β-subunit of HLA-DR antigen-overexpressed cells. The inset shows the chemical structure of the tridentate-based SHAL (SH7133) used in this study. SH7133 is composed of three recognition ligands that bind to neighboring sites on the surface of the target HLA-DR (highlighted in blue): 3-(2-([3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]oxy)-aniline-3-oxopropanionic acid) (Ct ligand), 4-[4-(4-chlorobenzyl)piperazino]-3-nitrobenzenecarboxylic acid (Cb ligand), and dansyl-l-valine (Dv ligand). (B) Schematic of the structure of SHAL-functionalized Dox NPs. (C) Representative TEM image of SHAL-functionalized Dox NPs. The mean number-average diameter (Dn) was found to be about 50 nm. (D) The plot of the intensity-average diameter (Dh) of SHAL-functionalized Dox NPs, as determined using the DLS method. The mean Dh of the Dox-encapsulated NPs was found to 82 ± 1 nm (polydispersity index = 0.205). (E) pH-dependent drug-release profiles of nontargeted and SHAL-functionalized Dox NPs in physiological conditions. (F) FACS binding assays for the Jurkat, Ramos, Daudi, and Raji cell lines: (i) biotin-functionalized SHAL (SH7129, labeled with PE-Cy5-labeled streptavidin) and (ii) rhodamine-labeled SHAL-functionalized PEG-PLGA NPs. (G) Representative CLSM images of Jurkat, Ramos, Daudi, and Raji cells: (i) unstained, (ii) stained with 200 nM of the biotin-functionalized SHAL SH7129 labeled with PE-Cy5-labeled streptavidin, and (iii) stained with rhodamine (Rhod)-labeled SHAL-functionalized PEG-PLGA NPs containing 200 nM of conjugated SHAL. The cells were stained at 4 °C for 30 min. (H) Representative time-dependent confocal images show the internalization of Raji cells pretreated with rhodamine-labeled SHAL-functionalized PEG-PLGA NPs after incubation at 37 °C for (i) 5 min, (ii) 30 min, and (iii) 60 min.