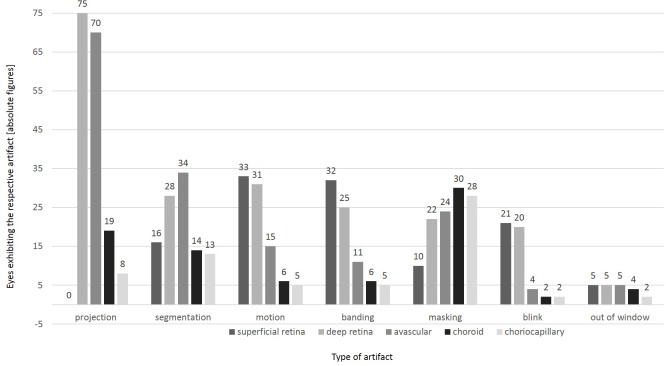
Fig 3. Frequencies of various artifacts in different segmentations of the OCTA scans.
Overall, the interpretability of the OCTA images was graded sufficient in 25% of assessments (19/75, 95% confidence interval (CI): 16%-37%) and excellent in 65% (49/75, 95% CI: 53%-76%), adding up to 91% of OCTA assessments deemed of an acceptable quality allowing for clinical interpretation (68/75, 95% CI: 82%-96%). Also, the presence of macular edema was associated with poorer interpretability: While 85.7% of OCTA images of eyes without ME were excellently interpretable, 76.9% of OCTA imaging results with a ME < 400 μm and 33.3% with a ME > 400 μm (p<0.01; Fisher`s exact test) were deemed of sufficient quality for clinical interpretability.