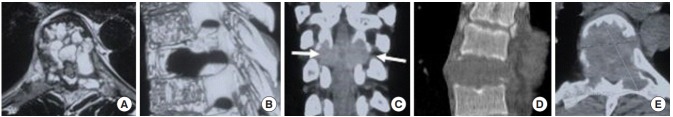
Fig. 2.
(A) Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging image shows multiple fluid pockets involving the vertebral body, adjacent pedicles and left lamina with posterior extension of lesion causing spinal canal compromise. (B) Sagittal 3-dimensional computed tomography (CT) image shows cortical breech, with posterior and epidural extension of the lesion. (C) Coronal CT arrows marks show distortion of pedicle margins bilaterally. (D) Sagittal CT image showing lytic lesion involving the entire height of vertebral body. (E) Axial CT cut shows thinned out sclerotic margins in anterior aspect of the lesion and grossly thinned out margins in the rest of vertebra.