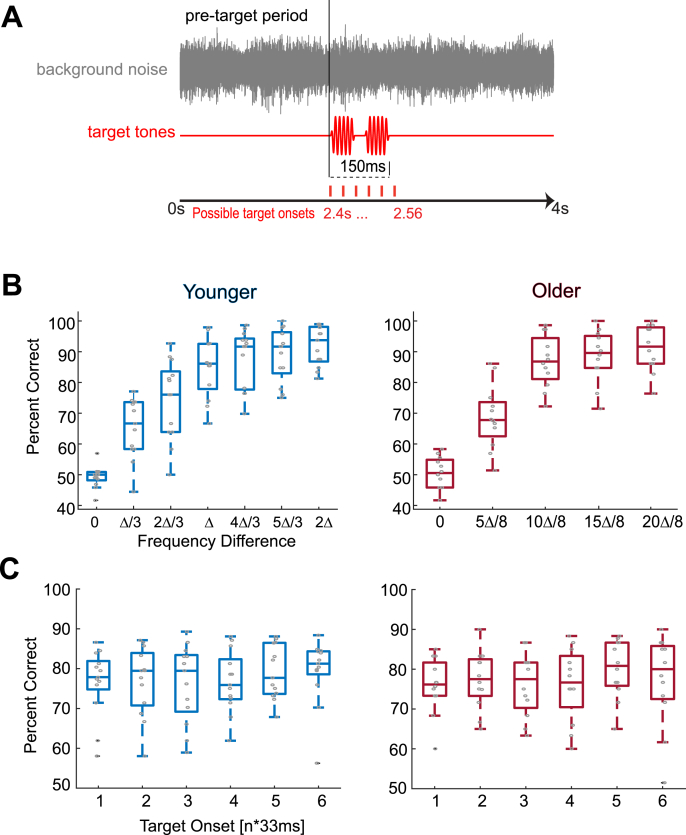
Fig. 1.
Auditory paradigm and task performance. (A) Auditory paradigm. Pure tone targets (50 ms duration, spaced 50 ms apart), were presented at one of six possible onsets against a continuous background noise cacophony. The second tone was kept at 1024 Hz while the first varied over 7 (younger adults) or 5 (older adults) levels of frequency difference, titrated around participants' own frequency difference limens, Δ. (B) Group level task performance as a function of stimulus level, averaged across target positions. Younger and older adults show comparable task performance. (C) Group level task performance as a function of target position, averaged across stimulus levels. There were no significant effects of target position on performance in either group and overall there was no significant difference between groups (across stimulus levels and target positions). Grey circles indicate individual subject data.