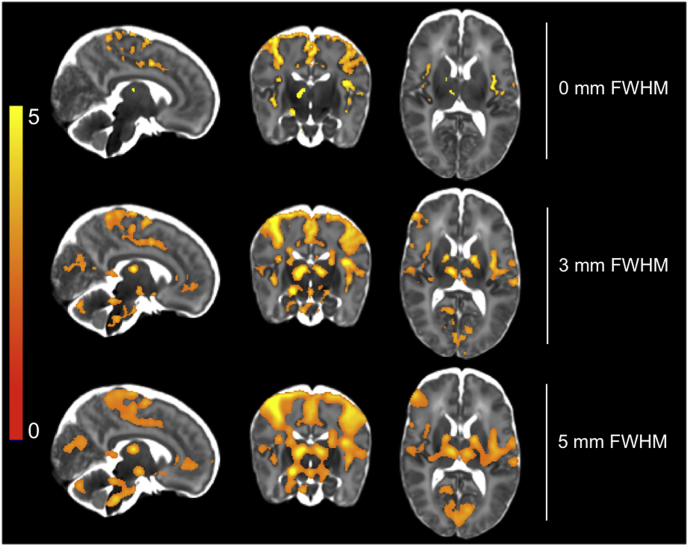
Fig. 10.
Comparison of the effects of spatial smoothing on t-statistics from the GLM output for all 15 subjects. Comparing thresholded (TFCE, default parameters, 5% FWER corrected) group activity maps, as spatial smoothing extent increased, the signal sensitivity increased in all ROIs, but the spatial specificity decreased. Not using spatial smoothing resulted in a lack of signal sensitivity in both cortical and subcortical structures. Using the 5 mm FWHM kernel, significant activity was incorrectly localised to non-grey matter regions, and distinct clusters of activity fused into massive clusters spanning several brain regions. Note, this spatial smoothing comparison was assessed using dHCP pipeline outputs only.