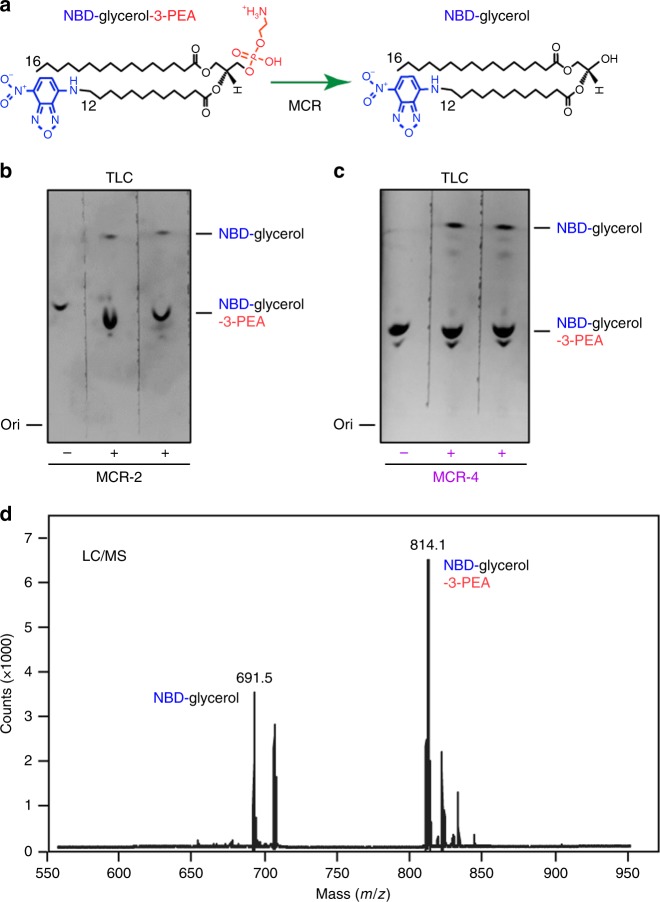
Fig. 3.
Scheme for enzymatic action of MCR-4. a A working model for the chemical reaction catalyzed by MCR family enzymes. This was adapted from our recent proposal9,10 with minor changes. In this model, MCR enzymes including MCR-4 removes the phosphoethanolamine (PEA) moiety from its alternative substrate NBD-glycerol-3-PEA, giving a putative intermediate of MCR-4-bound PEA and a final product of NBD-glycerol. NBD is indicated in blue, whereas PEA is highlighted in red. Thin layer chromatography (TLC)-based detection of enzymatic activities of MCR-2 (b) and MCR-4 (c) protein in the conversion of NBD-glycerol-PEA lipid substrate into NBD-glycerol For detection via TLC, the fluorescence signal of NBD-glycerol-3-PER (and/or NBD-glycerol) was captured under Epi blue light (455–485 nm) and a corresponding filter by the ChemiDoc MP imaging system (BioRad, CA, USA)60. d LC/MS analyses of MCR-4-mediated reaction products of NBD-glycerol-3-PEA. The spectrum of the substrate for MCR-4, NBD-glycerol-3-PEA appears at m/z of 814.1, whereas NBD-glycerol, the product of NBD-glycerol-3-PEA removing PEA (m/z, 123), is present at m/z 691.5