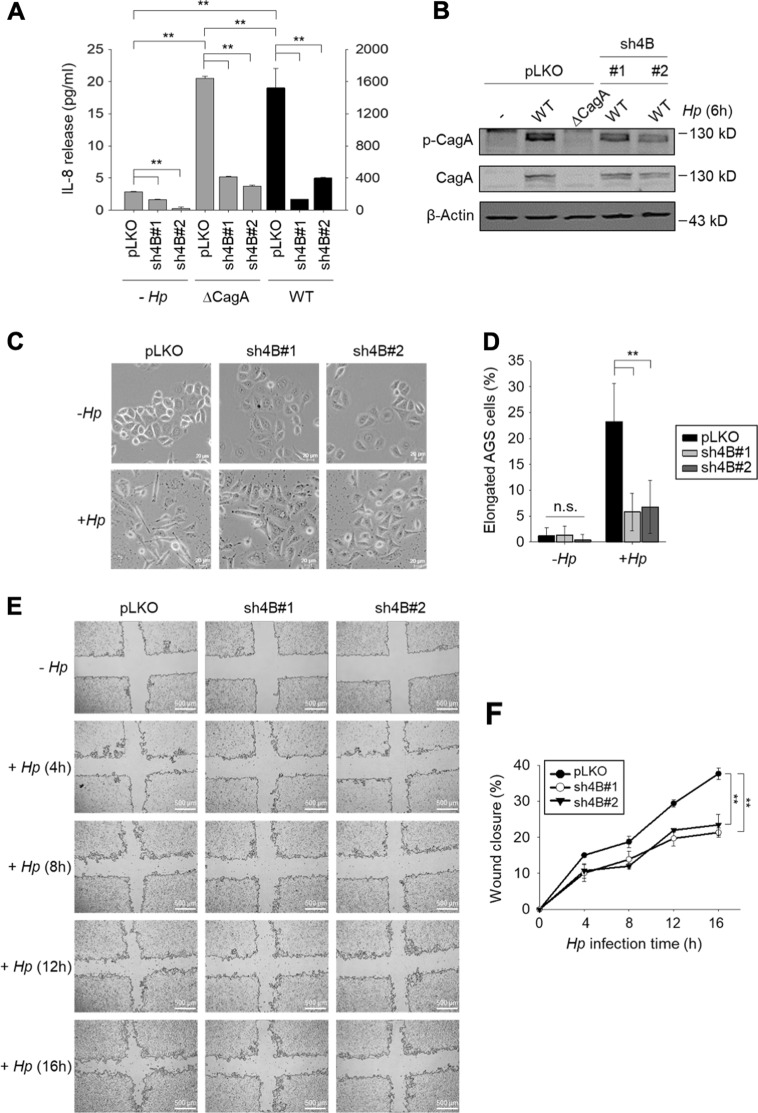
Fig. 5. H. pylori CagA is essential for KDM4B-mediated IL-8 production and hummingbird phenotype formation in infected cells.
a The CagA-positive H. pylori-induced IL-8 production mediated by KDM4B was significantly reduced in ∆cagA-infected AGS cells. Control and KDM4B-knockdown cells (sh4B#1 and sh4B#2) were either not infected or infected with WT (strain 26695) or ∆cagA at an moi of 50. IL-8 released into the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA. The values are means and SDs of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). b Detection of translocated phosphorylated CagA in KDM4B-knockdown cells was reduced. AGS cells were infected with WT or ∆cagA H. pylori at an moi of 50 for 6 h. Phospho-tyrosine antibody was used for determining phospho-CagA (p-CgaA) in immunoblotting assay. c Infection of KDM4B-knockdown cells with WT H. pylori had significantly reduced ability to display the hummingbird phenotype as compared with the control AGS cells. AGS cells were either not infected (−Hp) or infected with strain 26695 (+ Hp) at an moi of 50 for 3 h. Cells were visualized by phase-contrast microscopy to assess AGS cell morphology. Scale bar, 20 μm. d Quantification of the percentage of elongated cells from (c). e Infection of KDM4B-knockdown cells with WT H. pylori reduced cell migration. Wound healing effect of control (pLKO) and KDM4B-knockdown (sh4B#1 and sh4B#2) AGS cells at indicated post-infection time points. f The percentage of wound closure was measured from (e). The values are means and SDs of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01