Fig. 4.
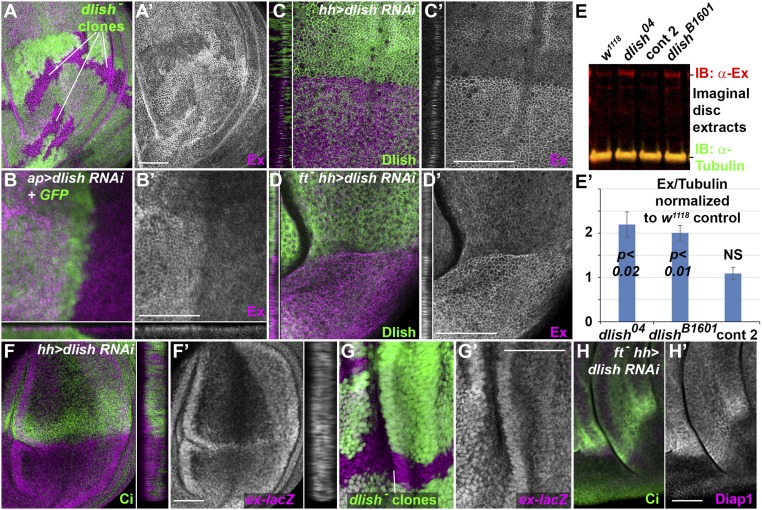
Loss of Dlish increases Ex in wing imaginal discs. (A) Increased subapical Ex (magenta, grey in A′) in dlish4506 homozygous clones (loss of green). (B–D) Increased subapical Ex (magenta, grey in B′–D′) after driving UAS-dlish-RNAi and UAS-GFP dorsally with ap-gal4 (B), or posteriorly with hh-gal4 in wild type (C) or ftfd homozygotes (D), marked by loss of Dlish (green). Cross-sections show subapical regions. (E) Example Western IB (E) and quantification from multiple IBs (E′) of Ex levels in extracts from w1118 control, phenotypically wild-type control 2 (Bloomington 51324) and dlish mutant discs. Quantifications were normalized to w1118 lanes from the same IB, and average changes (three extracts for each) compared using paired two-tailed t tests; NS, not significant; error bars = ±SD. (F and G) ex-lacZ expression (anti-βgal, magenta, gray in F′ and G′) is not altered by posterior, hh-gal4-driven UAS-dlish-RNAi (F, posterior marked by absence of green Ci; detail shows cross-section through disc) or by dlish04 mutant clones (G, marked by loss of green). (H) Expression of the Yki target Diap1 (magenta, grey in H′) is decreased by posterior, hh-gal4-driven UAS-dlish-RNAi in ftfd homozygote. (Scale bars: 50 μm.)